 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

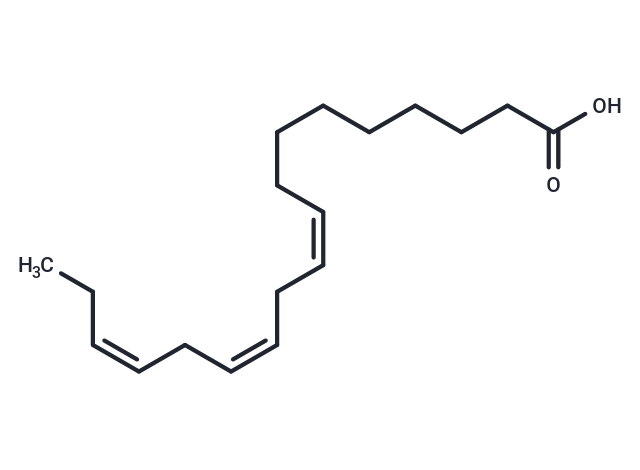
α-Linolenic Acid (ALA) is an essential fatty acid that cannot be synthesized by the human body and is obtained by isolating it from seed oils. α-Linolenic acid has been shown to improve memory, inhibit thrombosis, and lower blood lipids.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $33 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |

| Description | α-Linolenic Acid (ALA) is an essential fatty acid that cannot be synthesized by the human body and is obtained by isolating it from seed oils. α-Linolenic acid has been shown to improve memory, inhibit thrombosis, and lower blood lipids. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Osteosarcoma cells MG63, 143B and U2OS were treated with α-Linolenic Acid (10-200 µM) for 24 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. RESULTS: α-Linolenic Acid showed a highly inhibitory effect on cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner, with IC50 values of 51.69±0.14 µM in MG63 cells, 56.93±0.23 µM in 143B cells and 49.8±0.50 µM in U2OS cells.[1] METHODS: Breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 were treated with α-Linolenic Acid (25-100 µM) for 24 h. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometer. RESULTS: The percentage of apoptotic cells in the early (from 2.9% to 23.5% and from 5.5% to 16.7%, respectively) and late (from 0.6% to 3.4% and from 2.0% to 13.8%, respectively) apoptotic stages was significantly increased in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells treated with 100 µM α-Linolenic Acid. percentage significantly increased, which was significantly higher compared to untreated control cells. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study the therapeutic effect on colitis in mice, α-Linolenic Acid (150-300 mg/kg, dispersed in 0.25% Tween-20) was administered by gavage to HFHSD-fed BABL/c mice once daily for nine weeks. At the end of nine weeks, experimental colitis was induced by intracolonic injection of TNBS. RESULTS: Low α-Linolenic Acid administration significantly ameliorated TNBS-induced clinical manifestations, body weight loss, spleen weight loss, and histologic damage. In contrast, high α-Linolenic Acid administration did not improve colitis and even exacerbated symptoms.HFHSD exacerbated TNBS-induced colitis via the Th1/Th17 pathway. Low α-Linolenic Acid showed a protective effect against TNBS-induced colitis via the Th1/Th2/Th17 pathway. [3] |
| Synonyms | Linolenic acid, Alpha-Linolenic Acid |
| Molecular Weight | 278.43 |
| Formula | C18H30O2 |
| Cas No. | 463-40-1 |
| Smiles | CC\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCCCCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 0.914 g/cm3 at 25℃ (lit.) |
| Storage | store at low temperature,store under nitrogen | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 100 mg/mL (359.16 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 100 mg/mL (359.16 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 10 mg/mL (35.92 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.