 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

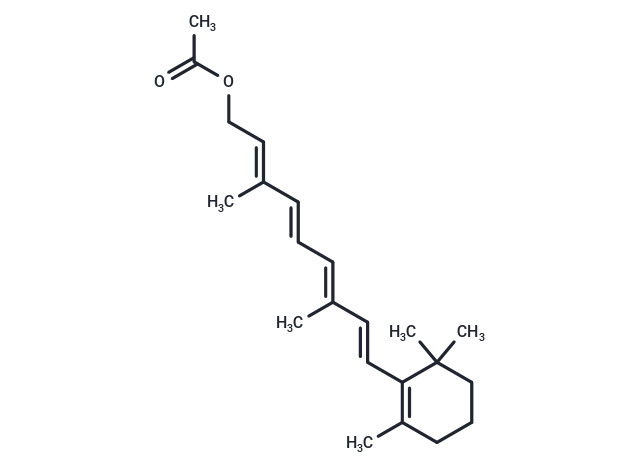
Retinyl acetate (Vitamin A acetate) is a group of unsaturated nutritional hydrocarbons, that contains retinal, retinol, retinoic acid, and several provitamins A carotenoids, among which beta-carotene is the most important.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $59 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $32 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Retinyl acetate (Vitamin A acetate) is a group of unsaturated nutritional hydrocarbons, that contains retinal, retinol, retinoic acid, and several provitamins A carotenoids, among which beta-carotene is the most important. |
| In vitro | Vitamin A deficiency impairs innate immunity by impeding normal regeneration of mucosal barriers damaged by infection, and by diminishing the function of neutrophils, macrophages, and natural killer cells. Vitamin A is also required for adaptive immunity and plays a role in the development of T both-helper (Th) cells and B-cells. Vitamin A deficiency diminishes antibody-mediated responses directed by Th2 cells, although some aspects of Th1-mediated immunity are also diminished. [1] |
| In vivo | Vitamin A acetate (VAA) (fed on an otherwise conventional diet) responds to 105 semiallogeneic cells (a suboptimal dose) in a host-versus-graft (HvG) reaction in mice, whereas mice on a conventional diet do not. [2] Vitamin A acetate can bring a solid and long-lasting state of tolerance induced by the intravenous injection into newborn CBA mice of lymphoid cells from (CBA X C57BL/10ScSn) F1 hybrids to an end, the effect of which is to increase the proportion of the moiety of the T-cell population that produces IL-2. [3] Vitamin A acetate-supplemented diet develops a positive skin reaction to purified protein derivative of mycobacteria in High-dose Mycobacterium bovis-infected mice, and their spleen cells show an increased IL-2 production in vitro. [4] |
| Synonyms | Vitamin A acetate, Retinyl (Retinol) Acetate, Retinol acetate |
| Molecular Weight | 328.49 |
| Formula | C22H32O2 |
| Cas No. | 127-47-9 |
| Smiles | C(=C/C(=C/C=C/C(=C/COC(C)=O)/C)/C)\C=1C(C)(C)CCCC1C |
| Relative Density. | 1.0474 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 60 mg/mL (182.65 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 40 mg/mL (121.77 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (6.09 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/Ethanol
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.