Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
ML-7 hydrochloride (ML-7 HCl) is a cell-permeable, reversible, effective, ATP-competitive, and specific inhibitor of myosin light chain kinase (Ki: 300 nM); also inhibits smooth-muscle myosin light chain kinase, PKA, and PKC.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $42 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $68 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $152 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $255 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $371 | - | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $482 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $46 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | ML-7 hydrochloride (ML-7 HCl) is a cell-permeable, reversible, effective, ATP-competitive, and specific inhibitor of myosin light chain kinase (Ki: 300 nM); also inhibits smooth-muscle myosin light chain kinase, PKA, and PKC. |
| Targets&IC50 | MLCK:0.3 μM(Ki), PKA:21 μM, PKC:42 μM |
| In vitro | Inhibition of MLCK by ML-7 induces activation of caspase-3 in adherent MCF-10A and MCF-10A Ras-transformed cells[2]. Its treatment results in a dose-dependent decrease in MLC20 phosphorylation and a corresponding increase in cell death of SMC(smooth muscle cells). The inhibitory effect of ML-7 on MLCK is highly selective. The Ki of ML-7 for MLCK is 0.3 μM, while its Ki for protein kinase A is 21 μM and for protein kinase C is 42 μM. Overexpressing Bcl-2 can protect cells against apoptosis induced by ML-7[4]. |
| In vivo | ML7 is able to improve Vascular endothelial dysfunction(VED) and atherosclerosis(AS) by regulating the expression of the tight junction (TJ) proteins zona occludens (ZO)-1 and occludin via mechanisms involving MLCK and MLC phosphorylation in high-fat diet-fed rabbits. ML7 decreases the expression of MLCK and MLC phosphorylation in the arterial wall of rabbits fed a high-fat diet and reduces lipid deposition lesions in AS rabbits[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | IKK-2 Assay: Recombinant human IKK-2 (residues 1-756) is expressed in baculovirus as an N-terminal GST-tagged fusion protein, and its activity is assessed using a time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay. In brief, IKK-2 (5 nM final) diluted in assay buffer (50 mM HEPES, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM CHAPS, pH 7.4, with 1 mM DTT and 0.01% w/v BSA) is added to wells containing various concentrations of compound or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) vehicle (3% final). The reaction is initiated by the addition of GST-IκBα substrate (25 nM final)/ATP (1 μM final), in a total volume of 30 μL. The reaction is incubated for 30 min at room temperature, then terminated by the addition of 15 μL of 50 mM EDTA. Detection reagent (15 μL) in buffer (100 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, and 0.1% w/v BSA) containing antiphosphoserine- IκBα-32/36 monoclonal antibody 12C2, labeled with W-1024 europium chelate, and an allophycocyanin-labeled anti-GST antibody is added, and the reaction is further incubated for 60 min at room temperature. The degree of phosphorylation of GST- IκBαis measured as a ratio of specific 665-nm energy transfer signal to reference europium 620-nm signal, using a Packard Discovery plate reader. |
| Cell Research | Cells are treated with vehicle alone, Blebbistatin, ML-7, ML-9, latrunculin A or Y-27632 in media without serum at varying concentrations and time points before being fixed or prepared for FACS analysis. Untreated cells are also serum starved for the duration of the inhibitor treatment. Stock solutions of each agent are made in DMSO (50 μM Blebbistatin, 5 mM LA), 50% ethanol (10 mM ML-7), 70% ethanol (20 mM ML-9) or water (20 mM Y-27632) and are maintained at -20°C.(Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | ML-7 HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 452.74 |
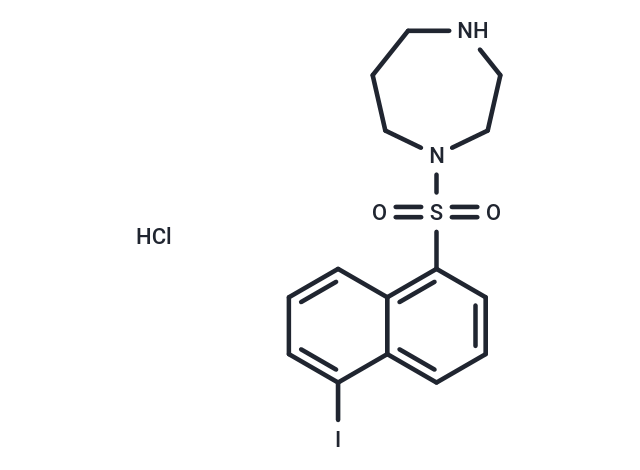
| Formula | C15H18ClIN2O2S |
| Cas No. | 110448-33-4 |
| Smiles | Cl.Ic1cccc2c(cccc12)S(=O)(=O)N1CCCNCC1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 60 mg/mL (132.53 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.