Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
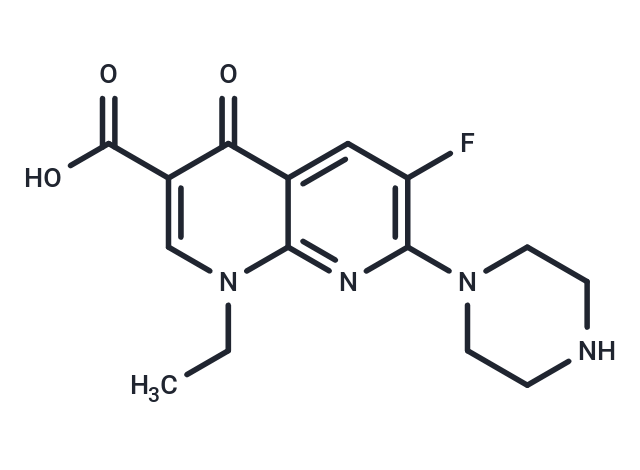
Enoxacin (NSC-629661) is a broad-spectrum 6-fluoronaphthyridinone antibacterial agent (fluoroquinolones) structurally related to nalidixic acid.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $34 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $78 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $113 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Enoxacin (NSC-629661) is a broad-spectrum 6-fluoronaphthyridinone antibacterial agent (fluoroquinolones) structurally related to nalidixic acid. |
| In vitro | Enoxacin, a fluoroquinolone used as an antibacterial compound, enhances the production of miRNAs with tumor suppressor functions by binding to the miRNA biosynthesis protein TAR RNA-binding protein 2 (TRBP). [1] Enoxacin binds to the DNA active site and alters the breakage/reunion activity of the enzyme. Enoxacin stimulates cleavage of both relaxed and supercoiled forms of DNA in the absence of ATP, whereas CcdB induces cleavage only after many cycles of ATP-dependent breakage and reunion. [2] Enoxacin dose dependently reduces the number of osteoclasts differentiating in mouse marrow cultures stimulated with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3), as well as markers of osteoclast activity, and the number of resorption lacunae formed on bone slices. Enoxacin inhibits osteoclast formation at concentrations where osteoblast formation is not altered. [3] Enoxacin dose-dependently reduces the number of multinuclear cells expressing tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) activity produced by RANK-L-stimulated osteoclast precursors. Enoxacin directly inhibits osteoclast formation without affecting cell viability by a novel mechanism that involves changes in posttranslational processing and trafficking of several proteins with known roles in osteoclast function. [4] Enoxacin is able to decrease cell viability, induce apoptosis, cause cell cycle arrest, and inhibit the invasiveness of prostate cancer (PCa) cell lines. Enoxacin is also effective in restoring the global expression of miRNAs in prostate cancer (PCa) cell lines. [5] |
| Synonyms | Pd107779, NSC 629661, CI 919, AT 2266 |
| Molecular Weight | 320.32 |
| Formula | C15H17FN4O3 |
| Cas No. | 74011-58-8 |
| Smiles | C(C)N1C=2C(C(=O)C(C(O)=O)=C1)=CC(F)=C(N2)N3CCNCC3 |
| Relative Density. | 1.388 g/cm3 |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 60 mg/mL (187.31 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.