 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

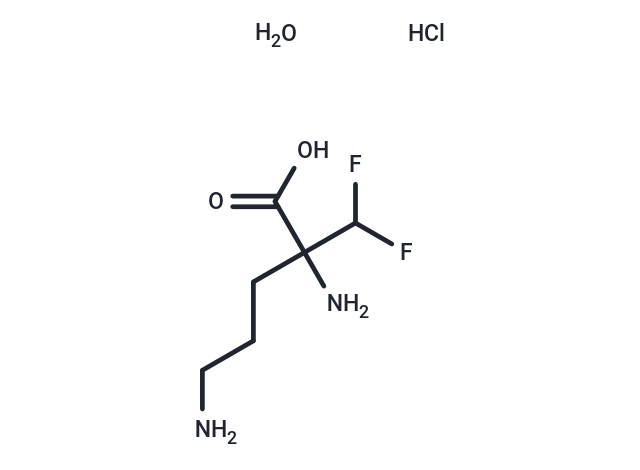
Eflornithine hydrochloride hydrate (DFMO hydrochloride hydrate) is a specific and irreversible inhibitor of the ornithine decarboxylase (ODC). Eflornithine hydrochloride hydrate has antitumor activity and has also been used in the hirsutism Eflornithine hydrochloride hydrate has antitumor activity and is also used in the treatment of hirsutism.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $42 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $123 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $179 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Eflornithine hydrochloride hydrate (DFMO hydrochloride hydrate) is a specific and irreversible inhibitor of the ornithine decarboxylase (ODC). Eflornithine hydrochloride hydrate has antitumor activity and has also been used in the hirsutism Eflornithine hydrochloride hydrate has antitumor activity and is also used in the treatment of hirsutism. |
| In vitro | When cultured cells are treated with α-difluoromethyl-Orn, an inhibitor of polyamine biosynthesis, production of hydrogen peroxide is suppressed and programmed cell death did not occur[1]. |
| In vivo | Eflornithine stands as the only novel compound registered for human African trypanosomiasis treatment in the past five decades, primarily serving as an alternative for cases resistant to melarsoprol involving Trypanosoma brucei gambiense. Additionally, a 15% eflornithine cream demonstrates efficacy superior to placebo in diminishing excessive, unwanted facial hair growth in patients, with 58% of individuals treated with eflornithine observing at least some improvement in facial hirsutism after 24 weeks, compared to 34% of those receiving placebo. Furthermore, the inhibitory effect on hair growth by eflornithine cream is significantly amplified when applied to mouse skin previously treated with microneedles. In hypertensive rats with coarctation, eflornithine treatment normalizes contractile responses to KCI and norepinephrine, and enhances relaxations to acetylcholine within 14 days, indicating its broader pharmacological utility. |
| Cell Research | BY2 cells are treated with or without cryptogein in the presence or absence of DFMO(Difluoromethylornithine) and monitered the effect of chemicals on cell growth. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | α-difluoromethylornithine hydrochloride hydrate, RMI-71782 hydrochloride hydrate, MDL-71782 hydrochloride hydrate, Eflornithine hydrochloride Monohydrate, Eflornithine hydrochloride, Difluoromethylornithine hydrochloride hydrate, DFMO hydrochloride hydrate |
| Molecular Weight | 236.64 |
| Formula | C6H15ClF2N2O3 |
| Cas No. | 96020-91-6 |
| Smiles | O.Cl.NCCCC(N)(C(F)F)C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.293g/cm3 |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 2.77 mg/mL (11.71 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 123.75 mg/mL (522.95 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.