 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

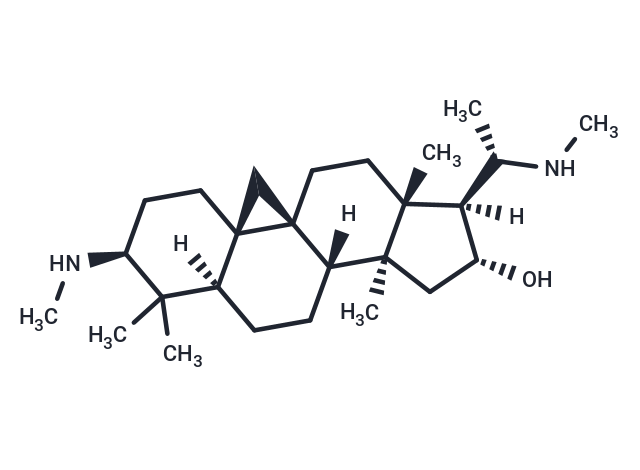
Cyclovirobuxine D (Bebuxine) is extracted from Buxus microphylla.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $37 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $56 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $78 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $113 | - | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $273 | Inquiry | Inquiry |
| Description | Cyclovirobuxine D (Bebuxine) is extracted from Buxus microphylla. |
| In vitro | The LD50 of Cyclovirobuxine D in mice is found to be 8.9 mg/kg (i.v.), 9.2 mg/kg (i.p.), and 293 mg/kg (p.o.). This compound is observed to reduce the weight of venous thrombosis in rats. In anesthetized pigs, Cyclovirobuxine D initiates coronary vasodilation, a mechanism associated with the release of nitric oxide in endothelial cells. Furthermore, it also improves cardiac failure induced by myocardial infarction in rats. |
| In vivo | Cyclovirobuxine D facilitates the utilization of intracellular Ca(2+) and prevents its efflux, thereby exerting protective effects against heart failure. It enhances the vitality of cardiomyocytes damaged by oxidation or hypoxia. Furthermore, it significantly reduces the infarct size caused by ligation of the coronary artery in rats. Cyclovirobuxine D also protects the endothelial cells of rat aortas from hypoxic damage and increases the release of NO within these cells. |
| Kinase Assay | MDA-MB-231 cells treated as indicated or tumor tissues are harvested and lysed in Mg2+ lysis buffer containing 50 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 10 mM MgCl2, 0.5 M NaCl, and protease inhibitor cocktail. Equal amounts of lysates are incubated with PAK-PBD beads at 4°C for 1 h. PAK-PBD beads are pelleted by centrifugation and washed with ish buffer containing 25 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 30 mM MgCl2, 40 mM NaCl. Active Rac1 is detected by western blotting. |
| Synonyms | Cyclovirobuxin D, CVB-D, Bebuxine |
| Molecular Weight | 402.66 |
| Formula | C26H46N2O |
| Cas No. | 860-79-7 |
| Smiles | [H][C@]1([C@H](C)NC)[C@H](O)C[C@@]2(C)[C@]3([H])CC[C@]4([H])[C@]5(C[C@@]35CC[C@]12C)CC[C@H](NC)C4(C)C |
| Relative Density. | 1.06 g/cm3 |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 14.23 mg/mL (35.34 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: Insoluble DMSO: Insoluble, Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.