Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Anti-AKT1 Polyclonal Antibody 2 is a Rabbit antibody targeting AKT1. Anti-AKT1 Polyclonal Antibody 2 can be used in WB.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μL | $221 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 100 μL | $373 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days | |
| 200 μL | $527 | 7-10 days | 7-10 days |
| Description | Anti-AKT1 Polyclonal Antibody 2 is a Rabbit antibody targeting AKT1. Anti-AKT1 Polyclonal Antibody 2 can be used in WB. |
| Synonyms | v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1, RAC-α, RAC-ALPHA, RAC, PRKBA, PKB-α, PKB-ALPHA, PKB, CWS6, AKT |
| Ig Type | IgG |
| Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat (predicted:Chicken,Dog,Pig,Cow,Rabbit,Sheep) |
| Verified Activity | 1. Tissue/cell: A549 cell; 4% Paraformaldehyde-fixed; Triton X-100 at room temperature for 20 min; Blocking buffer (normal goat serum) at 37°C for 20 min; Antibody incubation with (AKT1) polyclonal Antibody, Unconjugated (TMAB-00088) 1:100, 90 minutes at 37°C; followed by a FITC conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG antibody at 37°C for 90 minutes, DAPI (blue) was used to stain the cell nucleus. 2. Blank control: A549. Primary Antibody (green line): Rabbit Anti-AKT1 antibody (TMAB-00088) Dilution: 2 μg/10^6 cells; Isotype Control Antibody (orange line): Rabbit IgG. Secondary Antibody: Goat anti-rabbit IgG-FITC Dilution: 1 μg/test. Protocol The cells were incubated in 5% BSA to block non-specific protein-protein interactions for 30 min at room temperature. Cells stained with Primary Antibody for 30 min at room temperature. The secondary antibody used for 40 min at room temperature. 3. 25 μg total protein per Lane of various lysates probed with AKT1 polyclonal antibody, unconjugated (TMAB-00088) at 1:1000 dilution and 4°C overnight incubation. Followed by conjugated secondary antibody incubation at RT for 60 min. 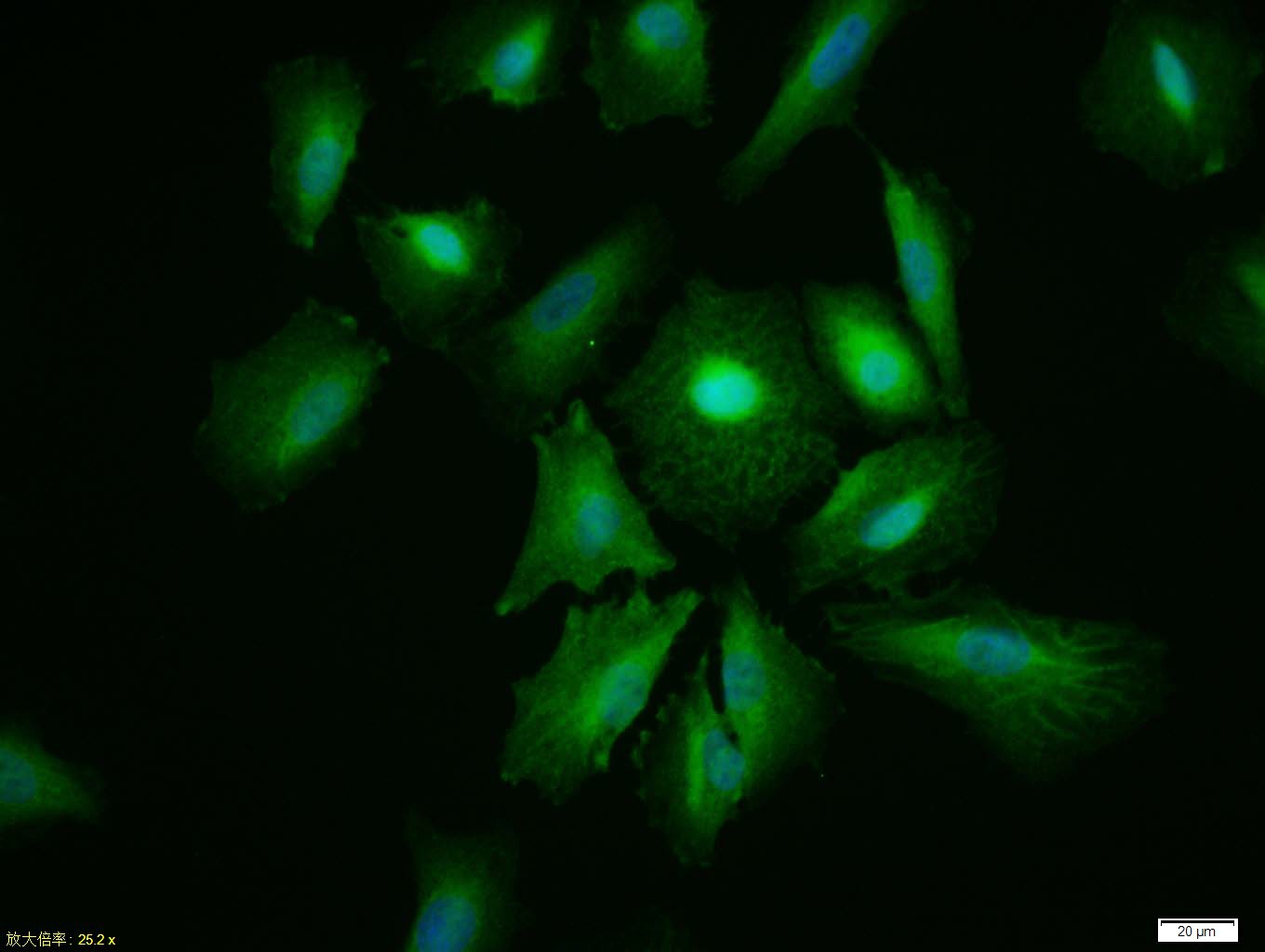 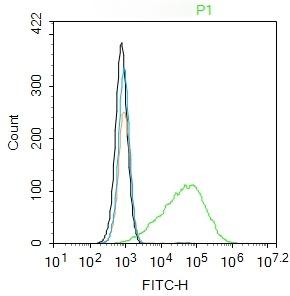 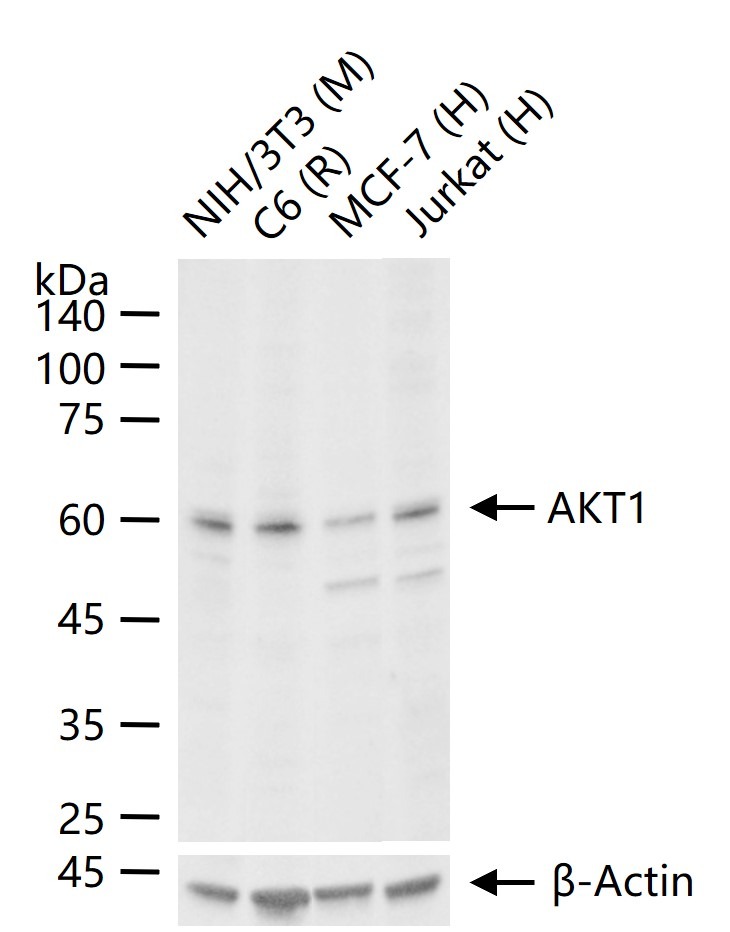 |
| Application | |
| Recommended Dose | WB=1:1000-5000 |
| Antibody Type | Polyclonal |
| Host Species | Rabbit |
| Subcellular Localization | Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cell membrane. Note=Nucleus after activation by integrin-linked protein kinase 1 (ILK1). Nuclear translocation is enhanced by interaction with TCL1A. Phosphorylation on Tyr-176 by TNK2 results in its localization to the cell membrane where it is targeted for further phosphorylations on Thr-308 and Ser-473 leading to its activation and the activated form translocates to the nucleus. |
| Tissue Specificity | Expressed in prostate cancer and levels increase from the normal to the malignant state (at protein level). Expressed in all human cell types so far analyzed. The Tyr-176 phosphorylated form shows a significant increase in expression in breast cancers dur |
| Construction | Polyclonal Antibody |
| Purification | Protein A purified |
| Appearance | Liquid |
| Formulation | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| Research Background | This gene encodes one of the three members of the human AKT serine-threonine protein kinase family which are often referred to as protein kinase B alpha, beta, and gamma. These highly similar AKT proteins all have an N-terminal pleckstrin homology domain, a serine/threonine-specific kinase domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain. These proteins are phosphorylated by phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). AKT/PI3K forms a key component of many signalling pathways that involve the binding of membrane-bound ligands such as receptor tyrosine kinases, G-protein coupled receptors, and integrin-linked kinase. These AKT proteins therefore regulate a wide variety of cellular functions including cell proliferation, survival, metabolism, and angiogenesis in both normal and malignant cells. AKT proteins are recruited to the cell membrane by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) after phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) by PI3K. Subsequent phosphorylation of both threonine residue 308 and serine residue 473 is required for full activation of the AKT1 protein encoded by this gene. Phosphorylation of additional residues also occurs, for example, in response to insulin growth factor-1 and epidermal growth factor. Protein phosphatases act as negative regulators of AKT proteins by dephosphorylating AKT or PIP3. The PI3K/AKT signalling pathway is crucial for tumor cell survival. Survival factors can suppress apoptosis in a transcription-independent manner by activating AKT1 which then phosphorylates and inactivates components of the apoptotic machinery. AKT proteins also participate in the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling pathway which controls the assembly of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4F (eIF4E) complex and this pathway, in addition to responding to extracellular signals from growth factors and cytokines, is disregulated in many cancers. Mutations in this gene are associated with multiple types of cancer and excessive tissue growth including Proteus syndrome and Cowden syndrome 6, and breast, colorectal, and ovarian cancers. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2020] |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide: human PKB |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Gene Name | AKT1 |
| Gene ID | |
| Protein Name | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| Uniprot ID | |
| Biology Area | Metabolism,AKT,Nuclear,Apoptosis,PKB / AKT |
| Function | AKT1 is one of 3 closely related serine/threonine-protein kinases (AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3) called the AKT kinase, and which regulate many processes including metabolism, proliferation, cell survival, growth and angiogenesis. This is mediated through serine and/or threonine phosphorylation of a range of downstream substrates. Over 100 substrate candidates have been reported so far, but for most of them, no isoform specificity has been reported. AKT is responsible of the regulation of glucose uptake by mediating insulin-induced translocation of the SLC2A4/GLUT4 glucose transporter to the cell surface. Phosphorylation of PTPN1 at 'Ser-50' negatively modulates its phosphatase activity preventing dephosphorylation of the insulin receptor and the attenuation of insulin signaling. Phosphorylation of TBC1D4 triggers the binding of this effector to inhibitory 14-3-3 proteins, which is required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. AKT regulates also the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen by phosphorylating GSK3A at 'Ser-21' and GSK3B at 'Ser-9', resulting in inhibition of its kinase activity. Phosphorylation of GSK3 isoforms by AKT is also thought to be one mechanism by which cell proliferation is driven. AKT regulates also cell survival via the phosphorylation of MAP3K5 (apoptosis signal-related kinase). Phosphorylation of 'Ser-83' decreases MAP3K5 kinase activity stimulated by oxidative stress and thereby prevents apoptosis. AKT mediates insulin-stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 at 'Ser-939' and 'Thr-1462', thereby activating mTORC1 signaling and leading to both phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and in activation of RPS6KB1. AKT is involved in the phosphorylation of members of the FOXO factors (Forkhead family of transcription factors), leading to binding of 14-3-3 proteins and cytoplasmic localization. In particular, FOXO1 is phosphorylated at 'Thr-24', 'Ser-256' and 'Ser-319'. FOXO3 and FOXO4 are phosphorylated on equivalent sites. AKT has an important role in the regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent gene transcription and positively regulates the activity of CREB1 (cyclic AMP (cAMP)-response element binding protein). The phosphorylation of CREB1 induces the binding of accessory proteins that are necessary for the transcription of pro-survival genes such as BCL2 and MCL1. AKT phosphorylates 'Ser-454' on ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), thereby potentially regulating ACLY activity and fatty acid synthesis. Activates the 3B isoform of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE3B) via phosphorylation of 'Ser-273', resulting in reduced cyclic AMP levels and inhibition of lipolysis. Phosphorylates PIKFYVE on 'Ser-318', which results in increased PI(3)P-5 activity. The Rho GTPase-activating protein DLC1 is another substrate and its phosphorylation is implicated in the regulation cell proliferation and cell growth. AKT plays a role as key modulator of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway controlling the tempo of the process of newborn neurons integration during adult neurogenesis, including correct neuron positioning, dendritic development and synapse formation. Signals downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI(3)K) to mediate the effects of various growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). AKT mediates the antiapoptotic effects of IGF-I. Essential for the SPATA13-mediated regulation of cell migration and adhesion assembly and disassembly. May be involved in the regulation of the placental development. Phosphorylates STK4/MST1 at 'Thr-120' and 'Thr-387' leading to inhibition of its: kinase activity, nuclear translocation, autophosphorylation and ability to phosphorylate FOXO3. Phosphorylates STK3/MST2 at 'Thr-117' and 'Thr-384' leading to inhibition of its: cleavage, kinase activity, autophosphorylation at Thr-180, binding to RASSF1 and nuclear translocation. Phosphorylates SRPK2 and enhances its kinase activity towards SRSF2 and ACIN1 and promotes its nuclear translocation. Phosphorylates RAF1 at 'Ser-259' and negatively regulates its activity. Phosphorylation of BAD stimulates its pro-apoptotic activity. |
| Molecular Weight | Theoretical: 56 kDa. |
| Stability & Storage | Store at -20°C or -80°C for 12 months. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Transport | Shipping with blue ice. |
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.