Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Cinnamic acid (β-Phenylacrylic acid) has potential use in cancer intervention,The concentration causing a 50% reduction of cell proliferation (IC50) ranged from 1 to 4.5 mM in glioblastoma, melanoma, prostate and lung carcinoma cells.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 41.00 |


| Description | Cinnamic acid (β-Phenylacrylic acid) has potential use in cancer intervention,The concentration causing a 50% reduction of cell proliferation (IC50) ranged from 1 to 4.5 mM in glioblastoma, melanoma, prostate and lung carcinoma cells. |
| In vivo | Oinnamic acid?exerts anti-diabetic activity by improving glucose tolerance in vivo and stimulating insulin secretion in vitro. |
| Animal Research | Non-obese type 2 diabetes was developed by injecting 90 mg/kg streptozotocin in 2-day-old Wistar pups. Cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde were administered orally to diabetic rats for assessing acute blood glucose lowering effect and improvement of glucose tolerance. Additionally, insulin secretory activity of cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde was evaluated in isolated mice islets. Cinnamic acid, but not cinnamaldehyde, decreased blood glucose levels in diabetic rats in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Oral administration of cinnamic acid with 5 and 10 mg/kg doses to diabetic rats improved glucose tolerance in a dose-dependent manner. The improvement by 10 mg/kg cinnamic acid was comparable to that of standard drug glibenclamide (5 mg/kg). |
| Source |
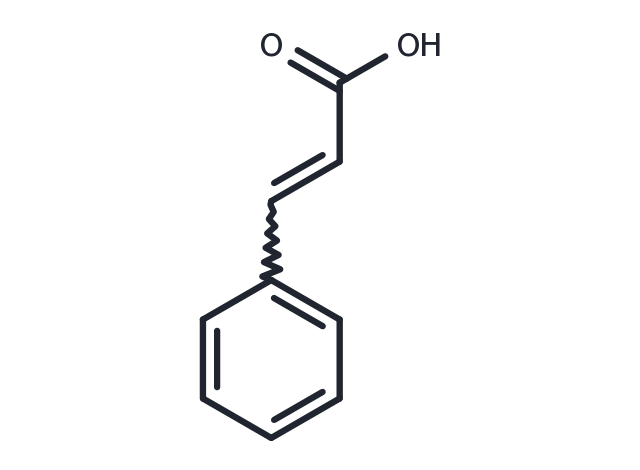
| Synonyms | 3-Phenylacrylic acid, β-Phenylacrylic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 148.16 |
| Formula | C9H8O2 |
| CAS No. | 621-82-9 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
Ethanol: 50 mg/mL (337.47 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Cinnamic acid 621-82-9 Metabolism Endogenous Metabolite inhibit b-Phenylacrylic acid 3-Phenylacrylic acid beta-Phenylacrylic acid β-Phenylacrylic acid Inhibitor inhibitor
