 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Amsilarotene (TAC101) inhibits the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product (RB) and increases the presence of 2 cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) inhibitors resulting in cell cycle arrest. This agent also causes a cytotoxic decline in the thymidylate synthase and cyclin A expression.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $36 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $88 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $143 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $247 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $355 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $488 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $97 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Amsilarotene (TAC101) inhibits the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product (RB) and increases the presence of 2 cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) inhibitors resulting in cell cycle arrest. This agent also causes a cytotoxic decline in the thymidylate synthase and cyclin A expression. |
| Targets&IC50 | RARα:2.4 nM (Ki), RARβ:400 nM (Ki) |
| In vitro | Preclinical models have shown that Amsilarotene(4-[3,5-bis(trimethylsilyl) benzamide] benzoic acid), an oral synthetic retinoid, has antitumor activity in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| In vivo | We conducted a phase I study in Japanese patients with advanced HCC to examine the pharmacokinetics, recommended dose, safety, and efficacy of Amsilarotene. The administered dose of Amsilarotene was 10 mg/day in four patients (level 1), 20 mg/day in six (level 2), and 30 mg/day in three (level 3). There was no dose-limiting toxicity at level 1. Only one patient each had dose-limiting toxicity at level 2 (grade 2 fatigue, recovery requiring eight or more consecutive days of rest) and at level 3 (grade 3 splenic vein thrombosis). Level 3 (30 mg/day) was considered the maximum tolerated dose and 20 mg/day the recommended dose by a panel of medical experts, placing maximum emphasis on safety. The most frequent adverse events were fatigue, headache, and dermal symptoms such as rash. Pharmacokinetic parameters in Japanese patients with HCC were similar to those in patients in the United States, most of whom were Caucasian. Although no patient had a complete or partial response, the disease control rate was 38.5%. In conclusion, the recommended dose of Amsilarotene for patients with HCC is 20 mg/day. Amsilarotene had an acceptable toxicity profile, warranting further evaluation in clinical trials. |
| Synonyms | TAC-101, TAC101, TAC 101 |
| Molecular Weight | 385.6 |
| Formula | C20H27NO3Si2 |
| Cas No. | 125973-56-0 |
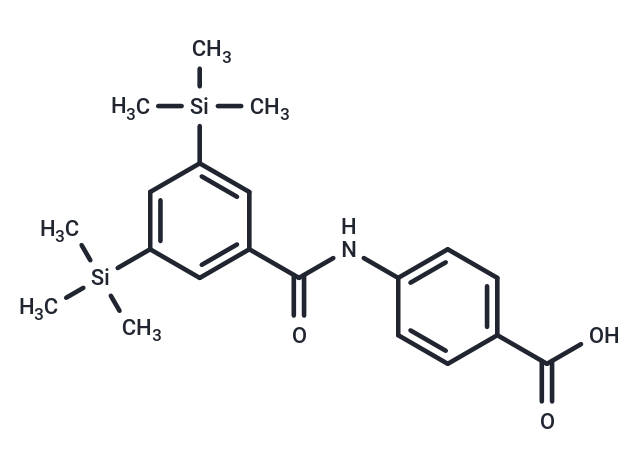
| Smiles | C[Si](C)(C)c1cc(cc(c1)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)Nc1ccc(cc1)C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.103g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 60 mg/mL (155.6 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: Insoluble | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (5.19 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.