Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Amsacrine (AMSA) (mAMSA) an antineoplastic agent which can intercalate into the DNA of tumor cells. Amsacrine also expresses topoisomerase inhibitor activity, specifically inhibiting topoisomerase II.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $39 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $55 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Amsacrine (AMSA) (mAMSA) an antineoplastic agent which can intercalate into the DNA of tumor cells. Amsacrine also expresses topoisomerase inhibitor activity, specifically inhibiting topoisomerase II. |
| In vitro | Amsacrine blocks HERG currents in HEK 293 cells and Xenopus oocytes in a concentration-dependent manner, with IC50 values of 209.4 nm and 2.0 μM, respectively. Amsacrine causes a negative shift in the voltage dependence of both activation ( 7.6 mV) and inactivation ( 7.6 mV). HERG current block by amsacrine is not frequency dependent[1]. In vitro studies of normal human lymphocytes with various concentrations of m-AMSA, show both increased levels of chromosomal aberrations, ranging from 8% to 100%, and increase SCEs, ranging from 1.5 times the normal at the lowest concentration studied (0.005 μg/mL) to 12 times the normal (0.25 μg/mL)[3]. Amsacrine-induced apoptosis of U937 cells is characterized by caspase-9 and caspase-3 activation, increased intracellular Ca2+ concentration, mitochondrial depolarization, and MCL1 down-regulation. Amsacrine induces MCL1 down-regulation by decreasing its stability. Further, amsacrine-treated U937 cells show AKT degradation and Ca2+-mediated ERK inactivation[4]. |
| In vivo | In animals treated with amsacrine (0.5-12 mg/kg), the frequencies of micronucleated polychromatic erythrocytes significantly increase at doses of 9 and 12 mg/kg. This study demonstrates for the first time that amsacrine exhibits high clastogenicity and low aneugenicity, while nocodazole exhibits high aneugenicity and low clastogenicity during mitotic phases in vivo[2]. |
| Synonyms | m-AMSA, CI-880, AMSA, acridinyl anisidide |
| Molecular Weight | 393.46 |
| Formula | C21H19N3O3S |
| Cas No. | 51264-14-3 |
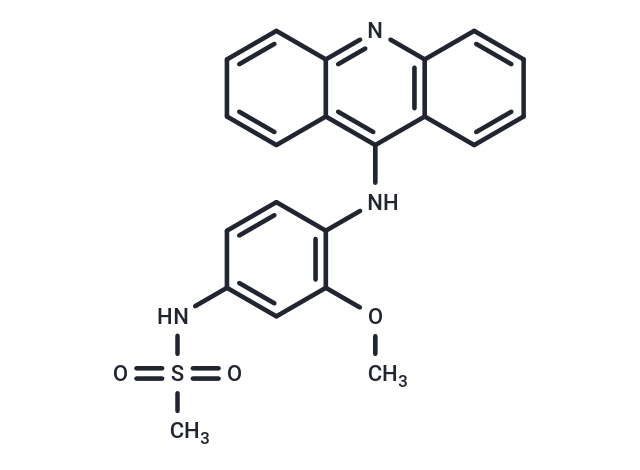
| Smiles | N(C=1C2=C(N=C3C1C=CC=C3)C=CC=C2)C4=C(OC)C=C(NS(C)(=O)=O)C=C4 |
| Relative Density. | 1.398 g/cm3 |
| Color | Yellow |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (127.08 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (5.08 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.