 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

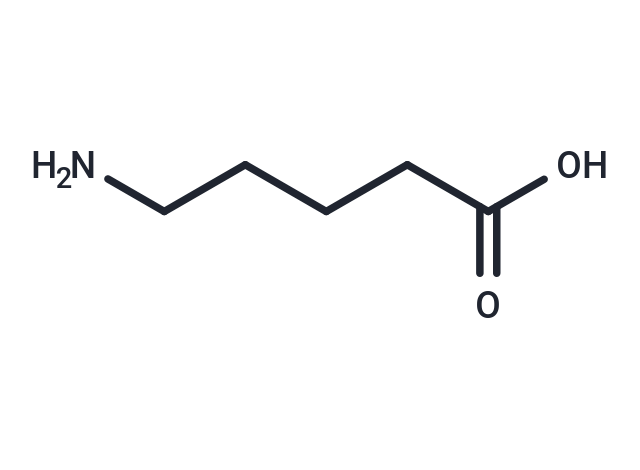
5-aminovalerate (or 5-aminopentanoic acid) is a lysine degradation product. It can be produced both endogenously or through bacterial catabolism of lysine. 5-aminovalerate is formed via the following multi-step reaction: L-lysine leads to cadverine leads to L-piperideine leads 5-aminovalerate . In other words it is a metabolite of cadaverine which is formed via the intermediate, 1-piperideine. Cadaverine is a foul-smelling diamine compound produced by protein hydrolysis during putrefaction of animal tissue. High levels of 5-aminovalerate in biofluids may indicate bacterial overgrowth or endogenous tissue necrosis. In most cases endogenous 5-aminovalerate is thought to be primarily a microbial metabolite produced by the gut or oral microflora, although it can be produced endogenously. 5-aminopentanoic acid is an in vivo substrate of 4-aminobutyrate:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase .
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $29 | Inquiry | Inquiry |
| Description | 5-aminovalerate (or 5-aminopentanoic acid) is a lysine degradation product. It can be produced both endogenously or through bacterial catabolism of lysine. 5-aminovalerate is formed via the following multi-step reaction: L-lysine leads to cadverine leads to L-piperideine leads 5-aminovalerate . In other words it is a metabolite of cadaverine which is formed via the intermediate, 1-piperideine. Cadaverine is a foul-smelling diamine compound produced by protein hydrolysis during putrefaction of animal tissue. High levels of 5-aminovalerate in biofluids may indicate bacterial overgrowth or endogenous tissue necrosis. In most cases endogenous 5-aminovalerate is thought to be primarily a microbial metabolite produced by the gut or oral microflora, although it can be produced endogenously. 5-aminopentanoic acid is an in vivo substrate of 4-aminobutyrate:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase . |
| In vitro | 5-aminovalerate is a normal metabolite present in human saliva, with a tendency to elevated concentration in patients with chronic periodontitis. Bacterial contamination and decomposition of salivary proteins is primarily responsible for elevated salivary levels. Beyond being a general waste product, 5-aminovalerate is also believed to act as a methylene homologue of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and functions as a weak GABA agonist. It is also known as an antifibrinolytic amino acid analog and so it functions as a weak inhibitor of the blood clotting pathway. |
| Molecular Weight | 117.15 |
| Formula | C5H11NO2 |
| Cas No. | 660-88-8 |
| Smiles | NCCCCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.2000 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Viscous |
| Storage | Pure form: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
| Solubility Information | DMSO: Slightly soluble |
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.