 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK is a pan-caspase inhibitor with irreversible properties; Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK is also an inhibitor of ubiquitin C terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1), which is irreversibly modified by targeting the UCHL1 active site.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $52 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $80 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $147 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $247 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $368 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $497 | - | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $693 | - | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $982 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $148 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK is a pan-caspase inhibitor with irreversible properties; Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK is also an inhibitor of ubiquitin C terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1), which is irreversibly modified by targeting the UCHL1 active site. |
| Targets&IC50 | SARS-CoV-2 Mpro:0.59 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human leukemia cells HL60 were treated with Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK (50 µM) and camptothecin (50 M) for 3 h. Cell morphology was observed by electron microscopy.
RESULTS: Cells treated with camptothecin exhibited typical apoptotic features including cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation and nuclear fragmentation.Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK combination treatment eliminated the camptothecin-induced apoptotic pattern. Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK alone did not affect cell morphology. [1] METHODS: Cholangiocarcinoma cells KKU100, KKU213A and KKU213B were pretreated with Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK (20 µM) for 1 h, followed by CH-MSCs (0%, 50% and 75%) for 24 h. Apoptosis was detected using Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK pretreatment prevented the apoptosis induced by CH-MSCs. [2] METHODS: Human ovarian teratoma cells PA-1 were treated with Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK (50 μM) and UVB (100 J/m2) for 16 h, and the expression levels of target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK eliminated PARP cleavage induced by UVB. [3] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To investigate whether in vivo administration of Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK prevents infection-induced preterm labor, a single intraperitoneal injection of Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK (10 mg/kg) was administered to CD1 mice in which preterm labor was induced by heat-killed group B streptococcus (HK-GBS).
RESULTS: Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK pretreatment delayed but did not prevent HK-GBS-induced preterm labor in a pregnant mouse model. [4] METHODS: To prevent LPS-induced acute lung injury, Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK (0.25 mg 15 min before LPS stimulation, 0.1 mg three times per hour) was injected intravenously into ICR mice with LPS-induced apoptosis and acute lung injury. RESULTS: Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK inhibited caspase-3 activity in lung tissues. Z-VAD(OMe)-FMK significantly prolonged the survival of mice. Apoptosis may play an important role in acute lung injury, and thus inhibition of caspase activity may provide a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of this disease. [5] |
| Cell Research | The human monocytic tumour cell line, THP.1 and the leukaemic T-cell line, Jurkat (clone E-6) were maintained in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal calf serum, 100 units/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin in an atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air at 37 °C. The cells were maintained in logarithmic growth phase by routine passage every 2–3 days. To induce apoptosis in THP.1 cells, 2×10^6 cells/ml were incubated either alone or in the presence of cycloheximide (25 μM) and TLCK (100 μM) as previously described. In order to assess the possible effects of various ICE-like protease inhibitors, THP.1 cells were also pretreated for 1 h with Z-VAD.FMK (10 μM), Ac-DEVD-CHO (20 μM) and Ac-YVAD-CHO (20 μM) before being exposed to the apoptotic stimulus. To induce apoptosis in Jurkat cells, 2×10^6 cells/ml were stimulated with 200 ng/ml anti-human Fas as described previously [1]. |
| Animal Research | Mice used in this study were 5- to 6-week-old (20 to 22 g) ICR males. Mice were injected with 30 mg/kg LPS from E. coli serotype O111:B4 through the tail vein. Z-VAD.fmk was dissolved at 2 mg/ml in 1% dimethyl sulfoxide in sterile saline, and administered to mice by the method of Rodriguez et al. A single intravenous injection of Z-VAD.fmk (0.25 mg) was made 15 minutes before LPS injection, followed by three intravenous injections of Z-VAD.fmk (0.1 mg each) per hour. Control mice were injected with the same volume of 1% DMSO in sterile saline [4]. |
| Synonyms | Z-Val-Ala-Asp(OMe)-FMK, Z-VAD-FMK |
| Molecular Weight | 467.49 |
| Formula | C22H30FN3O7 |
| Cas No. | 187389-52-2 |
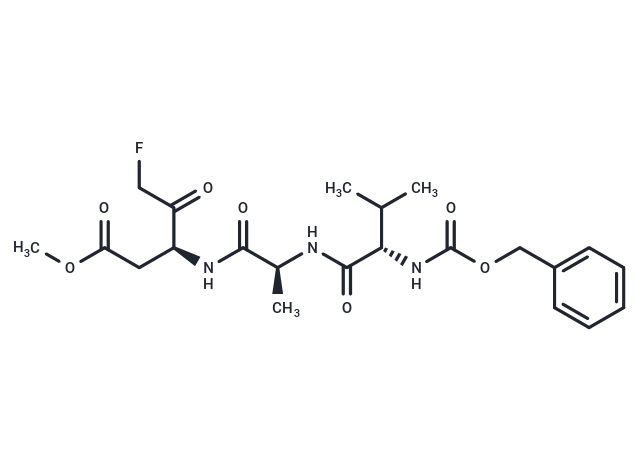
| Smiles | COC(=O)C[C@H](NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)OCc1ccccc1)C(C)C)C(=O)CF |
| Relative Density. | 1.214g/cm3 |
| Sequence | Z-Val-Ala-Asp(OMe)-FMK |
| Sequence Short | ZVA-D(OMe)-FMK |
| Storage | store at low temperature,keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 126.25 mg/mL (270.06 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 4.5 mg/mL (9.63 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.