Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


T-26c is highly potent and selective matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) inhibitor (IC50: 6.75 pM).
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 41.00 | |
| 2 mg | In stock | $ 58.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 97.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 155.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 263.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 447.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 646.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 98.00 |



| Description | T-26c is highly potent and selective matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) inhibitor (IC50: 6.75 pM). |
| Targets&IC50 | MMP13:6.75 pM (cell free) |
| In vitro | T-26c was the highly potent and selective MMP13 inhibitor with an IC50 value of 6.9 pM and more than 2600-fold selectivity over the other related metalloenzymes. Furthermore, the inhibitor was shown to be active in bovine nasal cartilage explants assay. T-26c significantly inhibited the breakdown of collagen (87.4% inhibition at 0.1 μM) in IL-1b and oncostatin M stimulated cartilage. |
| In vivo | Oral administration of the disodium salt formulations of T-26c to guinea pigs resulted in significant increases in AUC (8357 ng·h/mL) and Cmax (1445 ng/mL) compared with those of the free acid T-26c (AUC = 6478 ng·h/mL and Cmax = 911 ng/mL). The compound was well absorbed in all species at the oral dose of 10–20 mg/kg. |
| Kinase Assay | The MMP assay buffer consisted of 50 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.5), 10 mM CaCl2, 150 mM NaCl, and 0.05% Brij-35. The pro-MMPs were activated by preincubation with 1 mM aminophenylmercuric acetate (APMA) in assay buffer at 37 °C for 2 h (MMP-1, 2, 7, 8, 10, and 13) or 18 h (MMP-3 and 9). The TACE assay buffer consisted of 25 mM Tris–HCl (pH 9.0), 2.5 mM ZnCl2, and 0.005% Brij-35. The pro-MMPs were activated by preincubation with 1 mM aminophenylmercuric acetate (APMA) in assay buffer at 37 °C for 2 h (MMP-1, 2, 7, 8, 10, and 13) or 18 h (MMP-3 and 9). Enzyme inhibition assays were performed in an assay buffer containing enzymes and fluorescence peptide (Cy3-PLGLK(Cy5Q)AR-NH2 for MMPs, Cy3-PLAQAV(Cy5QL-2,3-diaminopropionic acid)-RSSSR-NH2 for TACE) in the presence of the various concentrations of inhibitors. Following incubation at 37 °C for 40 min, the reaction was terminated by addition of EDTA (pH 8.0). The increase in fluorescence as measured by Farcyte spectrofluorimeter. Enzyme activity (%) was determined as following equation: Enzyme activity (%) = (X - C)/(T - C) × 100, where X = the fluorescence count with inhibitor, T = the fluorescence count without inhibitor and C = the fluorescence count with EDTA. IC50 values of inhibitors were obtained with iterative fitting package. |
| Cell Research | Bovine nasal septum cartilage was sliced, and the slices were maintained in the medium of a 1:1 (v/v) mixture of Dulbecco's modified Eagle's MEM and Ham's F-12 medium (DMEM/F-12) containing 10 % fetal calf serum overnight. After confirming that the slices were not contaminated, they were cultured in DMEM/F-12 medium containing 20 μg/mL gentamycin, 50 μg/mL streptomycin, and 50 U/mL penicillin (culture medium) for 2 days at 37 °C. The cartilage slices were cut into small cubes (ca. 1mm3) and transferred individually into wells of a 96 well plate with 100 μL of culture medium. For the collagen degradation assay, the medium was supplemented with 10 ng/mL IL-1β and 50 ng/mL oncostatin M in the presence or absence of compounds. The cartilage was incubated for 2 weeks. The supernatants were harvested and replaced with fresh medium containing identical test compounds every 7 days. Supernatants of day 7 and day 14 were collected and stored at -20 °C until assay. At the end of the culture, the remaining cartilage was completely digested with papain. Hydroxyproline release in the media from each explant was determined as a measure of collagen degradation by use of chloramine T and p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde. The percentage of inhibitory activity against collagen degradation was calculated as follows: % of inhibition = [(% of collagen degradation with IL-1b and OSM) - (% of collagen degradation with IL-1β, OSM, and test sample)]/[(% of collagen degradation with IL-1β and OSM) - (% of collagen degradation without additives)] × 100. |
| Molecular Weight | 479.51 |
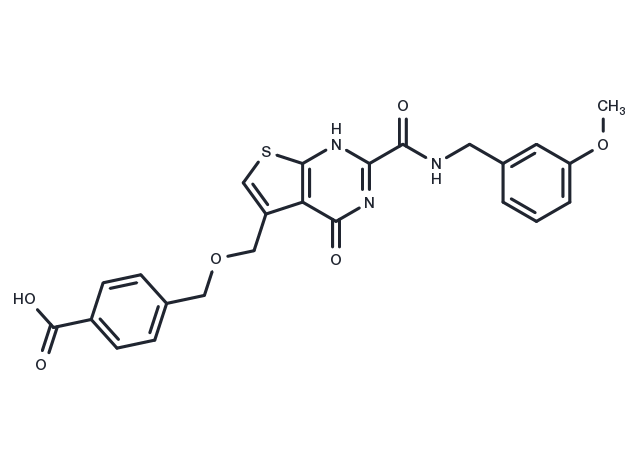
| Formula | C24H21N3O6S |
| CAS No. | 869296-13-9 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 12 mg/mL (25.03 mM)
H2O: Insoluble
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
T-26c 869296-13-9 Proteases/Proteasome MMP T26c Inhibitor Matrix metalloproteinases T 26c inhibit inhibitor
