 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ), as a well-known redox enzyme cofactor, PQQ can protect NS/PCs against glutamate toxicity associated with ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway,
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $32 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $43 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $60 | In Stock | - | |
| 500 mg | $138 | In Stock | - | |
| 1 g | $197 | Inquiry | Inquiry |
| Description | Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ), as a well-known redox enzyme cofactor, PQQ can protect NS/PCs against glutamate toxicity associated with ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway, |
| In vitro | Pyrroloquinoline quinone(PQQ) pretreatment showed its significant effect on protecting NS/PCs against glutamate-induced apoptosis/necrosis.?PQQ neuroprotection was associated with the decrease of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, the increase of glutathione (GSH) levels, and the decrease of caspase-3 activity.?In addition, pretreatment with PQQ also significantly enhanced the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) in the NS/PCs exposed to glutamate[1]. |
| In vivo | Pyrroloquinoline quinone(PQQ), a natural anti-oxidant present in a wide variety of human foods, exerted potent anti-fibrotic and ROS-scavenging activity in Balb/C mouse models of liver fibrosis. The antioxidant activity of PQQ was involved in the modulation of multiple steps during liver fibrogenesis, including chronic liver injury, hepatic inflammation, as well as activation of hepatic stellate cells and production of extracellular matrix. PQQ also suppressed the up-regulation of RACK1 in activated HSCs in vivo and in vitro. PQQ suppresses oxidative stress and liver fibrogenesis in mice[2]. |
| Animal Research | Healthy male Balb/C mice of 4–6 week were used to induce liver fibrosis and isolate primary HSCs.?The animals were obtained from SLAC Laboratory Animal Corp in SPF microbiological status.?All mice were maintained at 25°C with a 12 h dark/light cycle and completely randomly grouped.?For thioacetamide (TAA)-induced liver fibrosis, which has been shown to be closely resemble the panlobular and parenchymal fibrosis that is found in most human chronic liver disease , TAA was given by intraperitoneal injection ?at 200 mg/kg body weight 3 times each week for 8 weeks.?For bile duct ligation (BDL)-induced liver fibrosis, BDL was performed according to previous report , and mice were sacrificed 2 weeks later.?Administration of PQQ started on the second day when TAA was firstly given or BDL was performed, and PQQ was given at the dose of 0.3 mg/kg or 1 mg/kg by gastrogavage administration daily before mice were sacrificed.?Silymarin (150 mg/kg) was used as the positive control by gastrogavage administration daily.?Total number of 405 mice were used.?Mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation under anesthesia[2]. |
| Molecular Weight | 330.21 |
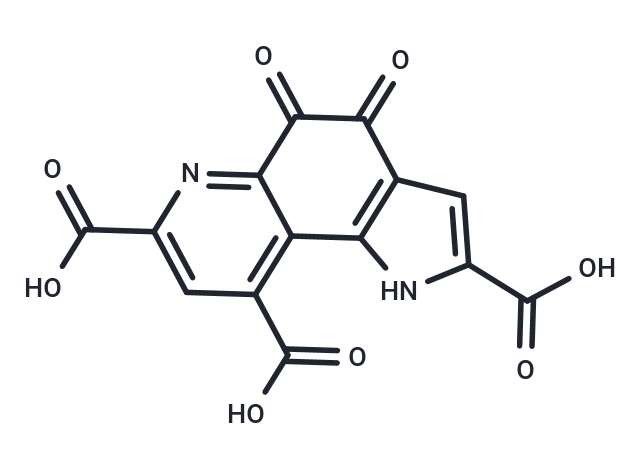
| Formula | C14H6N2O8 |
| Cas No. | 72909-34-3 |
| Smiles | OC(=O)C1=CC2=C(N1)C1=C(C=C(N=C1C(=O)C2=O)C(O)=O)C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.963 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 5 mg/mL (15.14 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 0.2 mg/mL (0.61 mM), Sonication is recommended. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.