 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

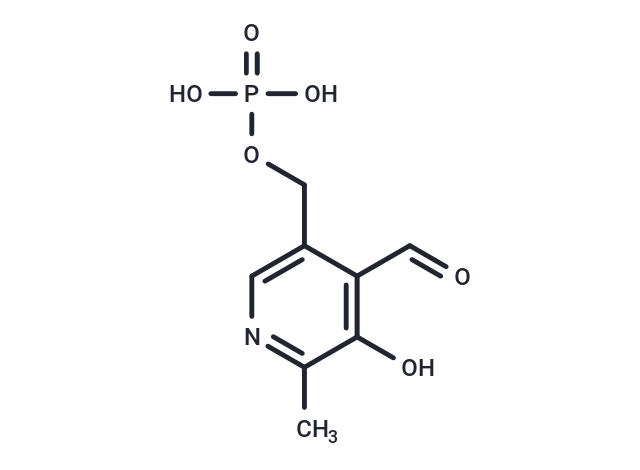
Pyridoxal phosphate (Vitamin B6 phosphate) is the active form of vitamin B6 and a coenzyme for many pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent enzymes. PLP is involved in numerous enzymatic transamination, decarboxylation and deamination reactions; it is necessary for the synthesis of amino acids and amino acid metabolites, and for the synthesis and/or catabolism of certain neurotransmitters, including the conversion of glutamate into gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and levodopa into dopamine. PLP can be used as a dietary supplement in cases of vitamin B6 deficiency. Reduced levels of PLP in the brain can cause neurological dysfunction.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $33 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Pyridoxal phosphate (Vitamin B6 phosphate) is the active form of vitamin B6 and a coenzyme for many pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent enzymes. PLP is involved in numerous enzymatic transamination, decarboxylation and deamination reactions; it is necessary for the synthesis of amino acids and amino acid metabolites, and for the synthesis and/or catabolism of certain neurotransmitters, including the conversion of glutamate into gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and levodopa into dopamine. PLP can be used as a dietary supplement in cases of vitamin B6 deficiency. Reduced levels of PLP in the brain can cause neurological dysfunction. |
| In vitro | Pyridoxal phosphate results in an immediate reduction in the rate of DNA synthesis. Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate severely inhibits the DNA Polymerase and RNase H. Conjugation to pyridoxal phosphate fully inhibits NEIL2. Pyridoxal phosphate-conjugated NEIL2 shows much lower activity than the intact enzyme over a wide range of enzyme/substrate ratios. After Pyridoxal phosphate conjugation, the ability of NEIL2 to bind the THF-ligand is completely lost. |
| Synonyms | Vitamin B6 phosphate, Pyridoxyl phosphate, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate, PLP, PAL-P |
| Molecular Weight | 247.14 |
| Formula | C8H10NO6P |
| Cas No. | 54-47-7 |
| Smiles | C(OP(=O)(O)O)C=1C(C=O)=C(O)C(C)=NC1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.638 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 250 mg/mL (1011.57 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 20.23 mM, Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: 2.5 mg/mL (10.12 mM), Sonication is recommeded. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.