 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

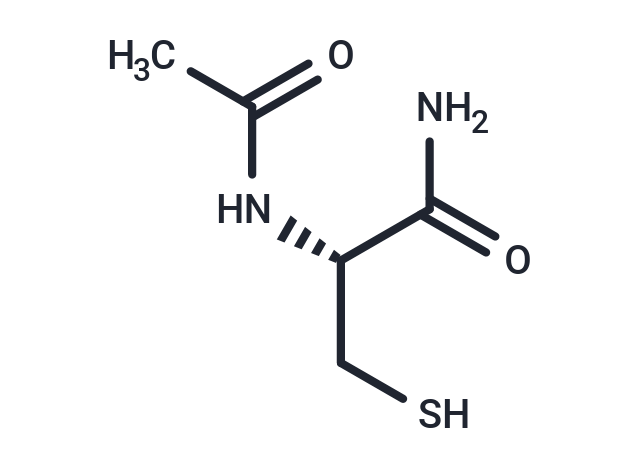
N-Acetylcysteine amide is a thiol antioxidant and a neuroprotective agent with cell permeability and blood-brain barrier permeability. N-Acetylcysteine amide reduces ROS production.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $39 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $64 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $97 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $197 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $313 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $478 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $1,050 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $58 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | N-Acetylcysteine amide is a thiol antioxidant and a neuroprotective agent with cell permeability and blood-brain barrier permeability. N-Acetylcysteine amide reduces ROS production. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human esophageal cancer cells KYSE30 and KYSE150 were treated with LAT1-IN-1 (1-100 mM) for 3 days, and cell viability was measured by MTT assay. RESULTS: LAT1-IN-1 treatment inhibited cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. [1] METHODS: HTR8 SVneo, JEG-3 and JAR cells were treated with LAT1-IN-1 (0.1-4 µM) for 24 h, and the expression levels of target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: LAT1 protein was significantly reduced after 24 h LAT1-IN-1 treatment, and LAT1-IN-1 could directly regulate the expression of LAT1. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To assay antitumor activity in vivo, LAT1-IN-1 (200 mg/kg) was administered intravenously to BALB/c nude mice bearing KYSE150 tumors once daily for 14 days. RESULTS: Daily treatment with LAT1-IN-1 for 14 consecutive days significantly delayed tumor growth. [1] |
| Cell Research | To determine effectiveness of NACA and NAC in protection of H9c2 cells from DOX-induced toxicity, cells were treated with NACA or NAC at 0.75 mM for 2 h followed by exposure to freshly prepared cell culture medium with DOX in presence or absence of NACA or NAC at designated concentrations. The concentrations of DOX were 0.25 μM, 0.75 μM, 2 μM, 5 μM, 20 μM, and 100 μM. The exposure durations were 24 h, 48 h, or 48 h. Cells incubated with NACA or NAC alone were used as the control[1]. |
| Animal Research | rats were randomly divided into three groups (n=6-8 animals/group): N-acetylcysteine amide?loaded pump (18.5?mg/kg/hr) and a single 150 mg/kg bolus intraperitoneal (IP) injection of NACA given (30 min post-injury) ?N-acetylcysteine amide?(18.5 mg/kg/hr) loaded pump and a single 150 mg/kg bolus injection of N-acetylcysteine amide?given IP (30 min post-injury) ?Vehicle loaded pump and?single vehicle bolus injection given IP (30 min post-injury).?Following random distribution of all animals into one of the three previous groups, experimenters were blinded to treatment group.?The osmotic mini pumps were assembled and implanted immediately after injury and remained in the animals for 7 days[2] |
| Molecular Weight | 162.21 |
| Formula | C5H10N2O2S |
| Cas No. | 38520-57-9 |
| Smiles | CC(=O)N[C@@H](CS)C(N)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.226 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 100 mg/mL (616.48 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 245 mg/mL (1510.39 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 5 mg/mL (30.82 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.