Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Lurasidone (SM-13496) is an antagonist of dopamine D2 and 5-HT7 receptors (IC50 = 1.68 and 0.495 nM, respectively) and a partial agonist of the 5-HT1A receptor (IC50 = 6.75 nM).
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $39 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $53 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $78 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $98 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $148 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $217 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Lurasidone (SM-13496) is an antagonist of dopamine D2 and 5-HT7 receptors (IC50 = 1.68 and 0.495 nM, respectively) and a partial agonist of the 5-HT1A receptor (IC50 = 6.75 nM). |
| Targets&IC50 | 5-HT7 receptor:0.495 nM (IC50), D2 receptor:1.68 nM (IC50), 5-HT1A receptor:6.75 nM (IC50) |
| In vitro | Lurasidone is administered once daily within the range of 40-160 mg/day for schizophrenia and 20-120 mg/day for bipolar depression, and its pharmacokinetic profile requires administration with food.?In adult healthy subjects and patients, a 40 mg dose results in peak plasma concentrations in 1-3 h, a mean elimination half-life of 18 h (mostly eliminated in the feces), and apparent volume of distribution of 6173 L;?it is approximately 99 % bound to serum plasma proteins.?Lurasidone's pharmacokinetics are approximately dose proportional in healthy adults and clinical populations within the approved dosing range, and this was also found in a clinical study of children and adolescents.?Lurasidone is principally metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 with minor metabolites and should not be coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inducers or inhibitors.?Lurasidone does not significantly inhibit or induce CYP450 hepatic enzymes[2]. |
| In vivo | In addition to its principal antagonist activity at dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT2A receptors, lurasidone has distinctive 5-HT7 antagonistic activity, and displays partial agonism at 5-HT1A receptors, as well as modest antagonism at noradrenergic α2A and α2C receptors.?Lurasidone is devoid of antihistaminic and anticholinergic activities[1]. |
| Synonyms | SM-13496 |
| Molecular Weight | 492.68 |
| Formula | C28H36N4O2S |
| Cas No. | 367514-87-2 |
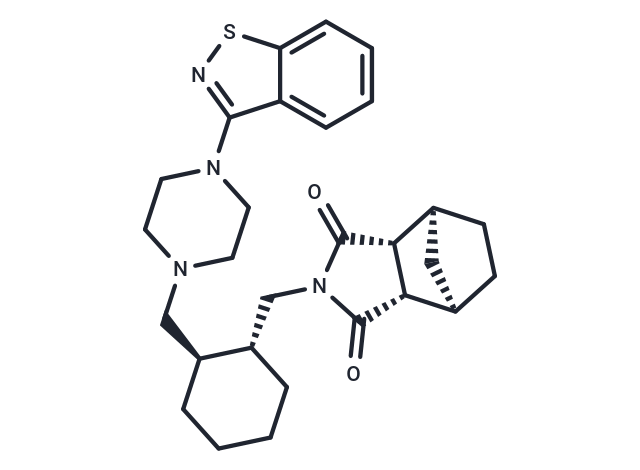
| Smiles | O=C1[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@H](C3)[C@H]2C(=O)N1C[C@@H]1CCCC[C@H]1CN1CCN(CC1)c1nsc2ccccc12 |
| Relative Density. | 1.273 g/cm3 |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | store under nitrogen | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 17.83 mg/mL (36.19 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+90% Corn Oil: 1.5 mg/mL (3.04 mM), Sonication is recommeded. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.