Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

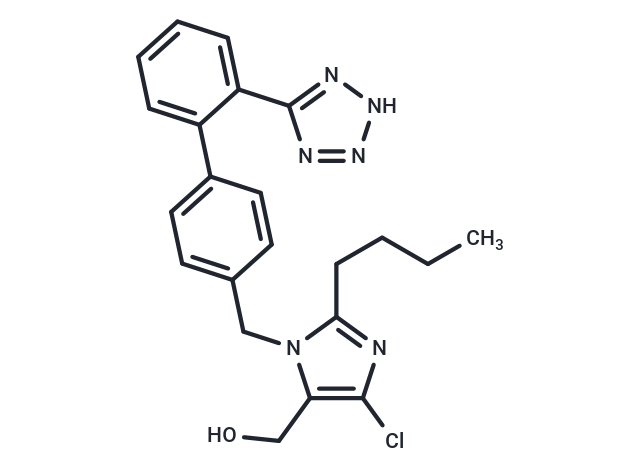
Losartan (DuP-753) is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Losartan (DuP-753) is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist. |
| Targets&IC50 | AT1 receptor:20 nM |
| In vitro | Losartan competes with the binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors, with an IC50 of 20 nM[1]. At 40 μM, losartan affects ISC and prevents the effect of ANGII on ISC[2]. It significantly reduces Ang II-mediated cell proliferation in endometrial cancer cells, with a greater antiproliferative effect when combined with anti-miR-155 compared to each drug alone[3]. |
| In vivo | Losartan (0.6 g/L, p.o.)-treated Fbn1C1039 g/+ mice show reduced distal airspace caliber compared to placebo-treated counterparts. The dosages of losartan and propranolol are titrated to achieve similar hemodynamic effects. Analysis of pSmad2 nuclear staining indicates that losartan antagonizes TGF-β signaling in the aortic wall of Fbn1C1039 g/+ mice, improving lung disease manifestations independently of hemodynamics[4]. Losartan (10 mg/kg, intraarterial injection) increases blood angiotensin levels by four- to sixfold. Losartan (10 mg/kg, i.p.) increases plasma renin levels by 100-fold, decreases plasma angiotensinogen levels to 24% of control, and leaves plasma aldosterone levels unchanged[5]. |
| Cell Research | An MTT assay is used to measure cell proliferation and viability. For the assay, 5000 cells in 200?μL media per well are seeded in a 96 well plate. After overnight incubation to allow for cell attachment, the medium is removed by suction. MTT at 1?mg/mL concentration in serum-free medium is added and then incubated for 4?h at 37°C. After removal of MTT solution, 100?μL of DMSO is added to dissolve formazan crystals. Absorbance at 570?nm and at 600?nm as a reference is then measured using a microplate reader. The difference in absorbance is thus relative to the extent of cell survival. |
| Alias | DuP-753 |
| Molecular Weight | 422.91 |
| Formula | C22H23ClN6O |
| Cas No. | 114798-26-4 |
| Smiles | CCCCC1=NC(Cl)=C(CO)N1CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C1=CC=CC=C1C1=NNN=N1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.35 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (106.41 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.