Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Lisinopril dihydrate (MK-521) is an orally bioavailable, long-acting angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor with antihypertensive activity.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $57 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $91 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in H2O) | $74 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Lisinopril dihydrate (MK-521) is an orally bioavailable, long-acting angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor with antihypertensive activity. |
| In vitro | Lisinopril significantly reduces left ventricular (LV) end-diastolic pressure (EDP), pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) and end-diastolic stress, addition of atenolol to Lisinopril further reduces EDP and PCWP. [1] Lisinopril is a structural homologue of enalaprilat, differing only in the second amino acid side chain. Lisinopril inhibits Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) in vitro, as well as after parenteral and oral administration to humans; its oral bioavailability is only 25-29%, but it has a longer duration of action than enalapril. [2] |
| In vivo | Lisinopril treated SHR rats has significantly raised total cholesterol levels compared to untreated spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) rats (+27%), but not compared to lisinopril treated Wistar Kyoto rats (WKY) rats. [3] Lisinopril is a long-acting angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor which blocks the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and reduces systemic blood pressure in rats. Lisinopril reduces the hydroxyproline level and inhibits accumulation of collagens in the pulmonary tissue of the treatment group (paraquat + lisinopril) and per-treatment group (lisinopril + paraquat) in rats. [4] Lisinopril results in preserved ultrafiltration volume (UF), glucose reabsorption (D 1 /D 0 glucose) and peritoneal thickness in rats. [5] Lisinopril (0.2 mg/kg twice a day for 10 days) protects the cell membrane integrity and lessens free radical-induced oxidant stress in guinea pig hearts. [6] |
| Synonyms | Renacor, MK-521 dihydrate |
| Molecular Weight | 441.52 |
| Formula | C21H35N3O7 |
| Cas No. | 83915-83-7 |
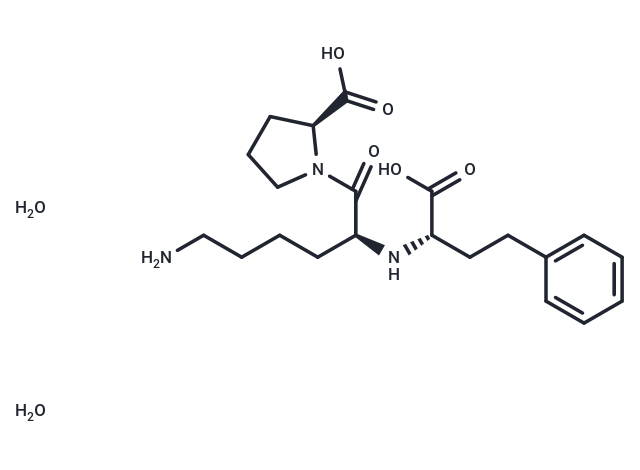
| Smiles | O.NCCCC[C@H](N[C@@H](CCc1ccccc1)C(=O)O)C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1C(=O)O.O |
| Relative Density. | 1.251 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 10 mM, Sonication is recommended. DMSO: Insoluble | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.