Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
KC7F2 is a potent HIF-1 pathway inhibitor with potential anti-cancer activity.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $43 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $52 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $93 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $173 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $255 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $332 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $54 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | KC7F2 is a potent HIF-1 pathway inhibitor with potential anti-cancer activity. |
| Targets&IC50 | HIF1α:20 μM |
| In vitro | KC7F2 inhibits HRE-driven transcription and decreases HIF-1α protein levels in LN229-HRE-AP cells. KC7F2 shows a dose-response cytotoxicity with IC50 of approximately 15 to 25 μM in cancer cells MCF7, LNZ308, A549, U251 mg, and LN229. In D54 mg glioma cells, KC7F2 inhibits colony formation, especially under hypoxia. [1] In hypoxic microglial cultures, KC7F2 downregulates the expression of TfR and DMT, and reduces the HIF-1α mediated iron accumulation. [2] |
| In vivo | KC7F2 significantly reduces the latent period in the pentylenetetrazole kindling rat model and increases the rate of spontaneous recurrent seizures during the chronic stage in the lithium-pilocarpine rat model. [3] |
| Kinase Assay | HIF transcriptional activity assay: Cells are incubated at 37 in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 and 21% O2 (normoxia) or 1% O2 (hypoxia) in a hypoxia workstation. The LN229-HRE-AP reporter cell line for HIF transcriptional activity is created by stably transfecting LN229 cells with the pACN188 plasmid, which contains an alkaline phosphatase gene driven by six HREs derived from the VEGF gene. |
| Cell Research | Cells are seeded onto 96-well plates (4 × 103/well) and cultured under normoxic (21% O2) and hypoxic (1% O2) conditions with different concentrations of KC7F2 for 72 h or treated for various times with 20 μM KC7F2. For proliferation analysis, cells are fixed with 50% trichloroacetic acid for 1 h at 4°C, followed by staining with 0.4% sulforhodamine B dissolved in 1% acetic acid for 30 min at room temperature. Plates are washed five times with 1% acetic acid to remove unbound dye. Bound dye is dissolved by adding 10 mM unbuffered Tris base. Cell proliferation is calculated by measuring OD values at 564 nm using a spectrophotometer.(Only for Reference) |
| Molecular Weight | 570.38 |
| Formula | C16H16Cl4N2O4S4 |
| Cas No. | 927822-86-4 |
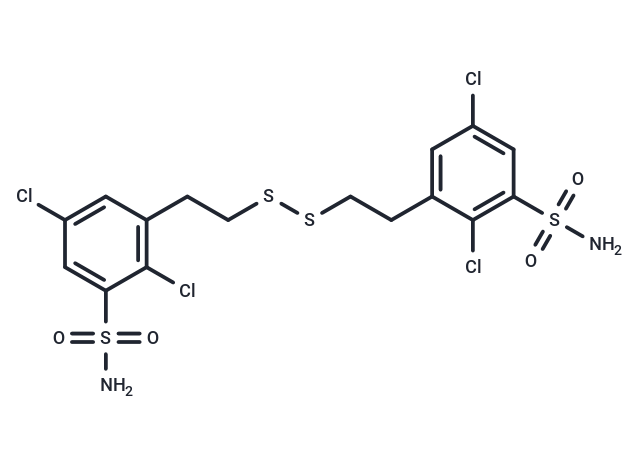
| Smiles | NS(=O)(=O)c1cc(Cl)cc(CCSSCCc2cc(Cl)cc(c2Cl)S(N)(=O)=O)c1Cl |
| Relative Density. | 1.583 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 57 mg/mL (99.93 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (3.51 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.