 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

GJ103 sodium salt is an active analog of GJ072, a read-through compound. It has been shown to reduce the surface tension of aqueous solutions, which makes it easier for molecules to move through the solution. It has also been shown to reduce the viscosity of aqueous solutions, which makes it easier for molecules to move through the solution. Additionally, it has been shown to reduce the pH of aqueous solutions, which can have a variety of effects on the biochemical and physiological processes of living organisms.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $47 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $76 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $153 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $265 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $289 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $422 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $43 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | GJ103 sodium salt is an active analog of GJ072, a read-through compound. It has been shown to reduce the surface tension of aqueous solutions, which makes it easier for molecules to move through the solution. It has also been shown to reduce the viscosity of aqueous solutions, which makes it easier for molecules to move through the solution. Additionally, it has been shown to reduce the pH of aqueous solutions, which can have a variety of effects on the biochemical and physiological processes of living organisms. |
| In vitro | GJ072 induces ATM kinase on both TGA and TAG stop codons and restored ATMpSer1981 autophosphorylation and SMC1pSer966 transphosphorylation as measured by FACS. GJ072 is active in A-T cells with a homozygous TAA mutation. GJ072 is able to induce detectable full-length ATM protein in treated A-T cells. Early structure-activity relationship studies generates eight active analogs of GJ072. Some GJ072 analogs (e.g., GJ103, GJ106, GJ109, and GJ111) consistently demonstrates their activities in all three PTCs by both FCATMpSer1981 and IRIF assays. GJ071 and GJ072 and some of their analogs (such as GJ103) have similar read-through activity as RTC13 or RTC14, but are more tolerable than RTC13 and RTC14 to A-T cells. GJ103 does not show obvious cytotoxicity in A-T cells at concentration as high as 300 μM. |
| In vivo | GJ103 sodium salt is water soluble, which will enable us to evaluate its in vivo activity by systematic administration. |
| Cell Research | Cell proliferation assay is used to measure cytotoxicity. Cells are seeded into a flat-bottom 96-well plate, including control wells containing complete growth medium alone as blank absorbance readings. After RTC treatment (GJ103), activated-XTT Solution is added into each well, and the cells are returned to the cell culture incubator for 12-14 hours. The absorbance is measured at 480 nM with relevant 630 nM to assess nonspecific readings. |
| Molecular Weight | 364.36 |
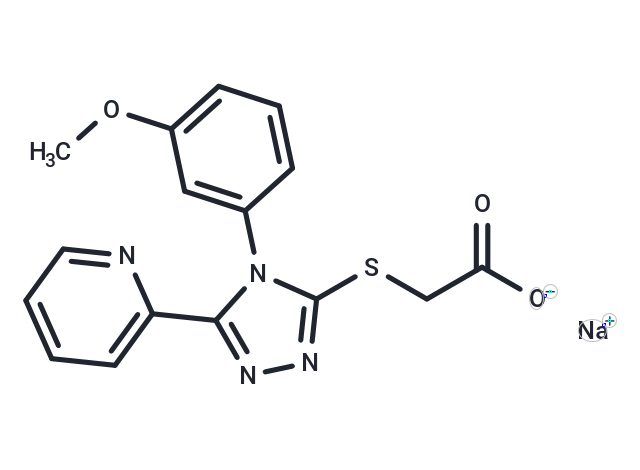
| Formula | C16H13N4NaO3S |
| Cas No. | 1459687-96-7 |
| Smiles | [Na+].COc1cccc(c1)-n1c(SCC([O-])=O)nnc1-c1ccccn1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: Soluble DMSO: 50 mg/mL (137.23 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: 2.5 mg/mL (6.86 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.