Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Dexmedetomidine is a Central alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonist. The mechanism of action of dexmedetomidine is as an Adrenergic alpha2-Agonist. The physiologic effect of dexmedetomidine is by means of General Anesthesia.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $39 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $64 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $97 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $155 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $262 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $43 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Dexmedetomidine is a Central alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonist. The mechanism of action of dexmedetomidine is as an Adrenergic alpha2-Agonist. The physiologic effect of dexmedetomidine is by means of General Anesthesia. |
| Targets&IC50 | α2-adrenoceptor:1.08 nM(Ki ) |
| In vitro | Dexmedetomidine has a relatively high ratio of α2/α1-activity (1620:1 as compared with 220:1 for clonidine) and, therefore, is considered a full agonist of the α2 receptor. This may result in more potent effects of sedation without unwanted cardiovascular effects from α1 receptor activation. The 2-h half-life of dexmedetomidine is nearly 4-fold shorter than that of clonidine, which increases the likelihood that a continuous infusion of dexmedetomidine might be useful for sedation. Dexmedetomidine also has minimum alveolar anesthetic concentration (MAC)-sparing properties, but its use as an anesthetic adjuvant has been complicated by persistent hypotension that has mandated IV fluid administration and vasopressor administration. In addition, its use in large doses is complicated by hypertension from α2 receptor-mediated vascular constriction. |
| Molecular Weight | 200.28 |
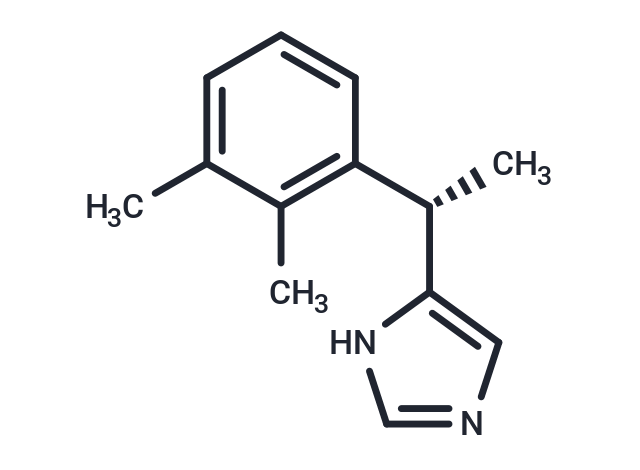
| Formula | C13H16N2 |
| Cas No. | 113775-47-6 |
| Smiles | [C@H](C)(C1=C(C)C(C)=CC=C1)C2=CN=CN2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.053g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 40 mg/mL (199.72 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (9.99 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.