Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

CRT0044876 (7-NO2-ICA) is a potent and selective APE1 inhibitor with IC50 of ~3 μM.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | 31 € | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | 45 € | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | 59 € | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | 140 € | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | 27 € | In Stock |
| Description | CRT0044876 (7-NO2-ICA) is a potent and selective APE1 inhibitor with IC50 of ~3 μM. |
| Targets&IC50 | APE1:3 μM |
| In vitro | CRT0044876 potently inhibits the AP endonuclease, 3'-phosphodiesterase and 3'-phosphatase activities of APE1, and exhibits the selectivity for the inhibition of exonuclease III family. CRT0044876 potentiates the cytotoxicity of several DNA base-targeting compounds with an accumulation of unrepaired AP sites. [1] CRT0044876, by inhibition of the BER pathway increases oxidative DNA damage temporally related to increased intracellular reactive oxygen species in an acidic tumor microenvironment, and thus results in cell cycle arrests and increased DNA double strand breaks, leading to cell death. [2] |
| Kinase Assay | AP site cleavage assay: BER reaction buffer comprises 40 mM HEPES–KOH (pH 7.8), 5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM DTT and 0.1 mM EDTA. A 10 μl AP site cleavage reaction comprised of BER buffer mix, purified protein (3.3 nM final concentration of APE1) and 0.75 ng reduced AP site double-stranded oligonucleotide. The mixture is incubated at 37°C for 1 h. A total of 1 μl of stop buffer (50% glycerol, 10 mM Tris–HCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.1% bromophenol blue and 0.1% Xylene cyanol) is added, and the sample mixture is denatured at 90–100°C for 2 min. The sample is then run on a 15% TBE Criterion? Pre-Cast Gel, with electrophoresis at a constant current of 30 mA for 30 min, and the radiolabeled substrate and reaction products are visualized using a phosphorImager. The inhibitory activity of potential APE1-targeting compounds are analyzed at drug concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 100 μM. The resolved radiolabeled bands are quantified using ImageQuant software analysis, and IC50 values are calculated by determining the concentration of the inhibitor that reduced APE1 activity to 50% of the control values. |
| Cell Research | HT1080 fibrosarcoma cells are grown in 2% RPMI medium [supplemented with penicillin 0.06 g/l, streptomycin 0.1 g/l (pH 7.0), 10% fetal bovine serum and 4 mM glutamine]. Only cells with a plating efficiency of ≥60% are used for clonogenic survival analysis. Tissue culture dishes (10 cm) are seeded with 500 cells per dish and the culture is maintained in a humidified incubator at 37°C in an atmosphere of 5% CO2 and 95% air. To evaluate the toxicity profile of putative APE1 inhibitors, various concentrations (100–500 μM) of inhibitor are added to the medium, and cultures were incubated for 7-10 days until cell colonies are formed. Colonies are fixed [75% (v/v) methanol, 25% (v/v) acetic acid] for 30 min and stained with crystal violet (1 mg/ml in distilled water) for 4 h at room temperature. Visible colonies are counted on a colony counter. (Only for Reference) |
| Alias | NSC 69877, 7-NO2-ICA, 7-Nitroindole-2-Carboxylic Acid |
| Molecular Weight | 206.15 |
| Formula | C9H6N2O4 |
| Cas No. | 6960-45-8 |
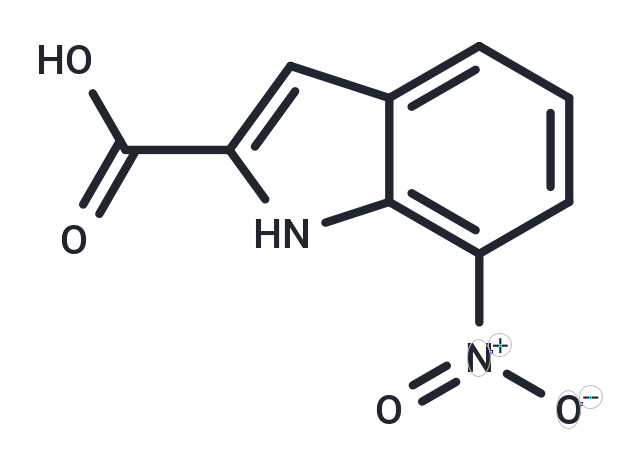
| Smiles | OC(=O)c1cc2cccc([N+]([O-])=O)c2[nH]1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.632 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 40 mg/mL (194.03 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 1 mg/mL (4.85 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.