Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Betaine chloride (Betaine hydrochloride) is an acidic form of betaine, a vitamin-like substance observed in grains and other foods; gains the amplification of DNA by decreasing the formation of secondary structure in GC-rich regions.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $42 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $59 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Betaine chloride (Betaine hydrochloride) is an acidic form of betaine, a vitamin-like substance observed in grains and other foods; gains the amplification of DNA by decreasing the formation of secondary structure in GC-rich regions. |
| In vitro | Exposure to increasing levels of Betaine hydrochloride significantly inhibits HeLa cell proliferation, as demonstrated by the MTT assay (p<0.05). The S phase cell percentage is notably higher in groups exposed to doses below 5 mg/mL compared to those subjected to higher doses, whereas Sub-G1 phase rates exhibit the reverse trend (p<0.05). Concentrations of Betaine hydrochloride above 5.0 mg/mL markedly induce apoptosis in HeLa cells (p<0.01). Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in low dose groups slightly exceeds that of the control group (p<0.05). Additionally, there's a noticeable synchrony and correlation in the expression levels of pro-apoptotic genes (Bax, P53, Caspase 3) and the anti-apoptotic gene (Bcl-2). Furthermore, upon inducing apoptosis signals, p53 and cyclin D1 are activated, potentially halting the cell cycle at either the G1/S or S/G2 checkpoints. |
| Synonyms | Betaine hydrochloride |
| Molecular Weight | 153.61 |
| Formula | C5H12ClNO2 |
| Cas No. | 590-46-5 |
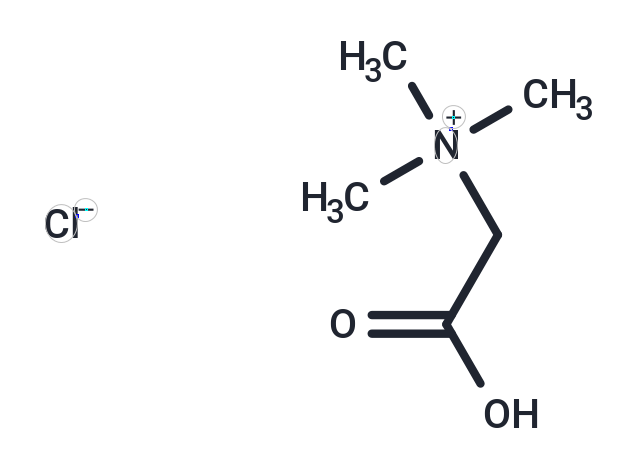
| Smiles | [Cl-].C[N+](C)(C)CC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1 g/cm3 |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 43 mg/mL (279.93 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.