Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

AZ6102 is a potent TNKS1/2 inhibitor that has 100-fold selectivity against other PARP family enzymes and shows IC50 of 5 nM for Wnt pathway inhibition in DLD-1 cells.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $37 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $59 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $97 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $231 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $369 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $549 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $66 | In Stock |
| Description | AZ6102 is a potent TNKS1/2 inhibitor that has 100-fold selectivity against other PARP family enzymes and shows IC50 of 5 nM for Wnt pathway inhibition in DLD-1 cells. |
| Targets&IC50 | TNKS1:5 nM, TNKS2:5 nM |
| In vitro | AZ6102 inhibits TNKS1 and TNKS2 in enzymatic assays and TCF4 reporter assays (<5 nM). AZ6102 inhibits proliferation of Colo320DM (GI50 ~40 nM), but has no anti-proliferative activity in the β-catenin mutant cell line HCT-116, or the BRCA mutant cell line MDA-MB-436. In Colo320DM, AZ6102 stabilizes axin2 protein and modulates Wnt target genes in a dose and time dependent manner both in vitro and in vivo[1]. |
| In vivo | Nude mice are administered 25 mg/kg of AZ-6102. The compound has a half-life of 4 hours and a CL of 24 mL/min.kg. Further analysis in mouse and rats shows that AZ-6102 has a moderate bioavailability at 12% and 18%, respectively. Western blot analysis for TNKS1, TNSK2 and Axin2 of treated DLD-1 cells shows that AZ-6102 had qualitatively stronger and longer lasting stabilization of TNSK1, TNSK2 and Axin2 than XAV-939 at lower concentrations (at 24, 48 and 72h). AZ-6102 has good pharmacokinetics in preclinical species with low Caco2 efflux (to avoid possible tumor resistance mechanisms). In addition, the compound can be formulated in a clinically relevant intravenous solution at 20 mg/mL using SBECD as an excipient at pH4. The results of AZ-6102 used as an i.v. probe compound to explore the in vivo effects of the inhibition of TNKS1 and TNSK2 on tumor xenografts and normal tissue are forthcoming[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | Sphingosine Kinase Assays: The IC50 values for ABC294640 and DMS are determined by a newly developed HPLC-based SK activity assay. In brief, the test compounds are incubated with recombinant SK1 or SK2 and NBD-Sph in the isozyme-selective assay buffers detailed below with 1 mg/ml fatty acid-free bovine serum albumin, 100 μM ATP, and 400 μM MgCl2. The product, i.e., NBD-S1P, is separated from NBD-Sph by HPLC as follows: Waters 2795 HPLC system with a Waters 2495 fluorescence detector, C8 Chromolith RP-8e column (100 × 4.6 mm), 1 ml/min mobile phase (acetonitrile/20 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH2.5, at 45:55). Fluorescence is monitored with excitation at 465 nm and emission at 531 nm. The ratio of NBD-S1P/(NBD-Sph + NBD-S1P) is used as a measure of SK activity. SK-isozyme selective assay buffers each contained 20 mM Tris, pH7.4, 5 mM EDTA, 5 mM EGTA, 3 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 5% glycerol, 1× protease inhibitors and 1× phosphatase inhibitors. For the SK1 assay buffer, 0.25% (final) Triton X-100 is added; and for the SK2 buffer, 1 M (final) KCl is added. Assays are run for 2 h at room temperature, and then a 1.5 volume of methanol is added to terminate the kinase reaction. After 10 min, the samples are centrifuged at 20,000 g to pellet the precipitated protein, and the supernatants are analyzed by HPLC. In experiments to determine the Ki for inhibition of SK2 by ABC294640, the ADP Quest assay system is used to measure kinase activity in the presence of varying concentrations of sphingosine and ABC294640. To determine the effects of ABC294640 on cellular SK activity, near-confluent MDA-MB-231 cells are serum-starved overnight, and then treated with varying concentrations of ABC294640. The cells are then incubated with [3H]sphingosine at a final concentration of 1 μM. The cells take up the exogenous sphingosine, which is converted to S1P via SK activity, and [3H]S1P is separated from [3H]sphingosine by extraction and quantified by scintillation counting. |
| Molecular Weight | 428.53 |
| Formula | C25H28N6O |
| Cas No. | 1645286-75-4 |
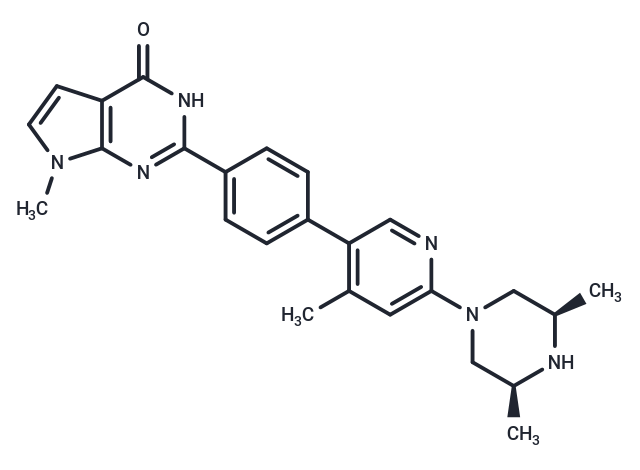
| Smiles | C[C@H]1CN(C[C@@H](C)N1)c1cc(C)c(cn1)-c1ccc(cc1)-c1nc2n(C)ccc2c(=O)[nH]1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.31 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 21.4 mg/mL (49.94 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.