

DM1(Mertansine), T1992, is a derivative of the natural alkaloid Maytansine. Maytansine is found in the genus Maytenus of the Celastraceae family and related plants, and it exhibits a potent ability to inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells. However, Maytansine is highly active and toxic, easily causing severe side effects. Therefore, medicinal chemists have modified Maytansine to obtain a series of derivatives. Among them, the most widely used are Mertansine DM1 and Mertansine DM4 (Ravtansine).
Mechanism of Action
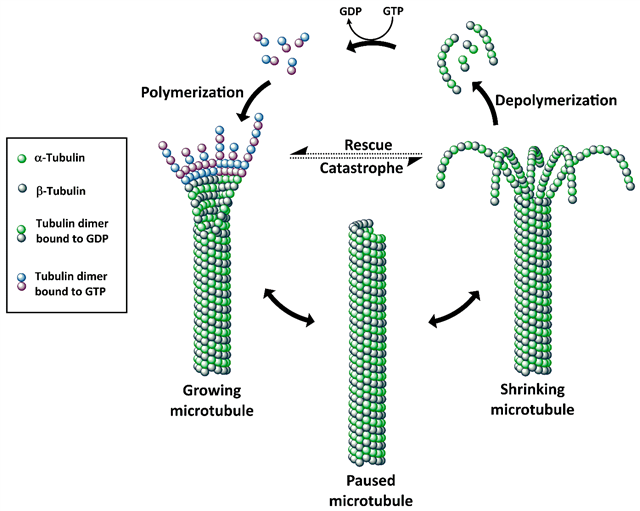
DM1 disrupts microtubules in rapidly dividing cancer cells, thereby interfering with chromosome segregation during mitosis. This interruption halts the cell cycle at the M phase, leading to apoptosis in cancer cells and exerting an anti-tumor effect.
Application
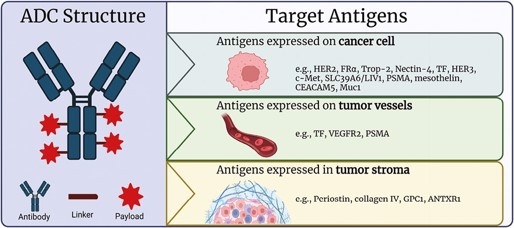
DM1 is primarily used as the cytotoxic component in Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs). ADCs generally consist of three parts: a monoclonal antibody drug targeting specific antigens, a cytotoxic drug and a linker connecting the antibody and the cytotoxic agents ("Payload"). The antibody locates tumor cells, and the linker allows the antibody to carry the cytotoxic agents into the tumor cells. The toxic small molecule typically disrupts DNA, microtubule proteins, etc., thereby preventing tumor cell division and killing the cells. DM1 is precisely such a toxic small molecule.
Physical and Chemical Properties
DM1 is a solid at normal temperature and pressure. It can dissolve in common organic solvents such as ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, and alcohol. However, its solubility is poor in ether-based solvents and water. It should be noted that DM1 is unstable in solution, so it is recommended to prepare and use the solution immediately.
TargetMol's new molecules
N6F11 | |
|
|
A novel inhibitor targeting the non-druggable tyrosine phosphatase PTPN2/N1; Can enhance tumor sensitivity to INF-γ and promote T cell activation and function; Published in Nature (IF: 64.8) | A novel and specific ferroptosis inducer; Can initiate T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity without causing immune cell ferroptosis; Published in Science Translational Medicine (IF: 17.1) |
