 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

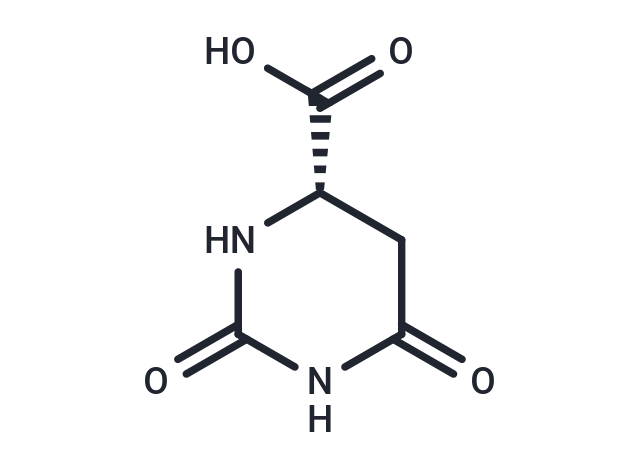
L-Dihydroorotic acid, also known as (S)-4,5-dihydroorotate or dihydro-L-orotate, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha amino acids and derivatives. Within the cell, L-dihydroorotic acid is primarily located in the cytoplasm and mitochondria. L-Dihydroorotic acid exists in all eukaryotes, ranging from yeast to humans. L-Dihydroorotic acid participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, L-Dihydroorotic acid can be biosynthesized from ureidosuccinic acid; which is catalyzed by the enzyme cad protein. In addition, L-Dihydroorotic acid and quinone can be converted into orotic acid; which is mediated by the enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone), mitochondrial. In humans, L-dihydroorotic acid is involved in the pyrimidine metabolism pathway. L-Dihydroorotic acid is also involved in several metabolic disorders, some of which include UMP synthase deficiency (orotic aciduria), the mngie (mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalopathy) pathway, Beta ureidopropionase deficiency, and dihydropyrimidinase deficiency.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $39 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $98 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $143 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | L-Dihydroorotic acid, also known as (S)-4,5-dihydroorotate or dihydro-L-orotate, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha amino acids and derivatives. Within the cell, L-dihydroorotic acid is primarily located in the cytoplasm and mitochondria. L-Dihydroorotic acid exists in all eukaryotes, ranging from yeast to humans. L-Dihydroorotic acid participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, L-Dihydroorotic acid can be biosynthesized from ureidosuccinic acid; which is catalyzed by the enzyme cad protein. In addition, L-Dihydroorotic acid and quinone can be converted into orotic acid; which is mediated by the enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone), mitochondrial. In humans, L-dihydroorotic acid is involved in the pyrimidine metabolism pathway. L-Dihydroorotic acid is also involved in several metabolic disorders, some of which include UMP synthase deficiency (orotic aciduria), the mngie (mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalopathy) pathway, Beta ureidopropionase deficiency, and dihydropyrimidinase deficiency. |
| Synonyms | L-Hydroorotic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 158.11 |
| Formula | C5H6N2O4 |
| Cas No. | 5988-19-2 |
| Smiles | OC(=O)[C@@H]1CC(=O)NC(=O)N1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.523 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (316.24 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (12.65 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.