 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

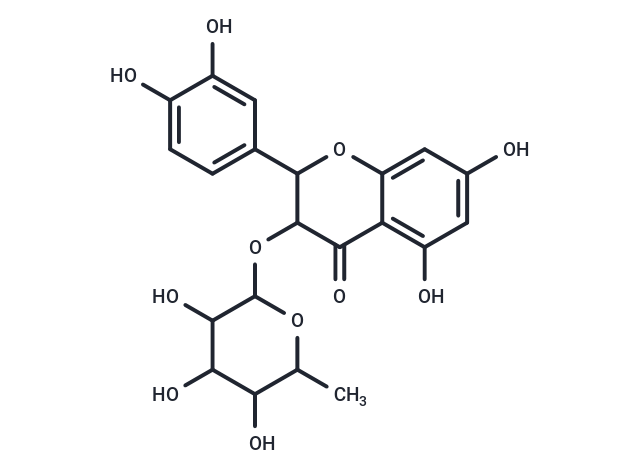
Isoastilbin is a dihydroflavonol glycoside compound found in Rhizoma Smilacis glabrae and Astragalus membranaceus. Isoastilbin inhibits glucosyltransferase (GTase) with an IC50 value of 54.3 μg/mL and possesses anti-acne and tyrosinase inhibition properties. Additionally, isoastilbin demonstrates neuroprotective, antioxidation, antimicrobial, and anti-apoptotic properties, indicating potential for Alzheimer's disease research.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $68 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $173 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $257 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $419 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $581 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $768 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $197 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Isoastilbin is a dihydroflavonol glycoside compound found in Rhizoma Smilacis glabrae and Astragalus membranaceus. Isoastilbin inhibits glucosyltransferase (GTase) with an IC50 value of 54.3 μg/mL and possesses anti-acne and tyrosinase inhibition properties. Additionally, isoastilbin demonstrates neuroprotective, antioxidation, antimicrobial, and anti-apoptotic properties, indicating potential for Alzheimer's disease research. |
| Targets&IC50 | GTase:54.3 μg/mL (IC50) |
| In vitro | The crude extracts were assayed for antimicrobial activities against Streptococcus sobrinus and for glucosyltransferase (GTase) inhibition. Fourteen extracts inhibited the growth of S. sobrinus by more than 50% and six extracts inhibited GTase activity by more than 50% at a concentration of 100 μg/ml. Koompassia malaccensis (kempas) extracts showed 90% depression of S. sobrinus growth and 80% inhibition of GTase activity at a concentration of 100 μg/ml. Kempas crude extracts were subjected to column chromatography using Sephadex LH-20 and then preparative high-performance liquid chromatography to isolate four compounds A, B, C, and D. These compounds were identified as taxifolin and the flavanonol rhamnoside isomers neoastilbin, astilbin, and Isoastilbin, respectively, from 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra and other two-dimensional NMR techniques (COSY, HMBC, and HMQC). Each compound depressed the growth of S. sobrinus over a concentration range of 9.3242.7 μg/ml and showed GTase inhibitory activity with IC50 values in the range 27.4-57.3 μg/ml[1] |
| Molecular Weight | 450.39 |
| Formula | C21H22O11 |
| Cas No. | 54081-48-0 |
| Smiles | CC1OC(OC2C(Oc3cc(O)cc(O)c3C2=O)c2ccc(O)c(O)c2)C(O)C(O)C1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.74 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 25 mg/mL (55.51 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 1 mg/mL (2.22 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.