 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

V-9302 (V9302) is a competitive antagonist of transmembrane glutamine flux that selectively and potently targets the amino acid transporter ASCT2 (IC50: 9.6 uM).
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $35 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $56 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $81 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $147 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $230 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $370 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $93 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | V-9302 (V9302) is a competitive antagonist of transmembrane glutamine flux that selectively and potently targets the amino acid transporter ASCT2 (IC50: 9.6 uM). |
| Targets&IC50 | ASCT2:9.6 μM (in HEK-293 cells) |
| In vitro | V-9302 inhibited ASCT2-mediated glutamine uptake in human cells in a concentration-dependent fashion and exhibited a 100-fold improvement in potency (IC50 V-9302 = 9.6 μM) over gamma-L-glutamyl-p-nitroanilide (GPNA; IC50 = 1000 μM). The EC50 concentrations for the four colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines exposed to V-9302 ranged from approximately 9-15 μM. |
| In vivo | Following a single dose of V-9302 (75 mg/kg, 4 h), [18F]-4F-glutamine uptake in tumors was reduced by approximately 50% to levels below background uptake in healthy muscle. Over the treatment course, V-9302 (75 mg/kg/day, 21 days) prevented tumor growth compared to vehicle controls in both HCT-116 and HT29 xenograft models. |
| Cell Research | Live-cell amino acid uptake assays using HEK293 cells were carried out in 96-well plates. 96-well plates were coated with poly-D-lysine prior to the assay. Cells were plated at a density of 35,000 cells per well 24 h prior to carrying out the assay. Each set of conditions was replicated at least three times, technically and biologically. Cells were washed three times with 100 μL of assay buffer (containing 137 mM NaCl, 5.1 mM KCl, 0.77 mM KH2PO4, 0.71 mM MgSO4.7H2O, 1.1 mM CaCl2, 10 mM D-glucose, and 10 mM HEPES) to remove cell media. 3H-amino acid (500 nM) in the same buffer was added concomitantly with V-9302 and allowed to incubate for 15 min at 37 oC. For ASCT2-mediated 3H-glutamine uptake assays, 5 mM of the system-L inhibitor 2-amino-2-norbornanecarboxylic acid (BCH) was added and the assay buffer was adjusted to pH 6.0. For selectivity studies, no BCH was added and the assay was conducted at pH 7.4. Following the incubation period, the 3H-glutamine/inhibitor was removed and the cells were washed three times with assay buffer. The cells were then lysed by the addition of 50 μL of 1 M NaOH. For reading, 150 μL of scintillation fluid was added and the plates were counted on a scintillation counter. IC50 was calculated using GraphPad Prism. |
| Animal Research | Animal handling methods for PET imaging studies were conducted as reported. Prior to imaging, animals were allowed to acclimate to facility environment for at least 1 h in a warmed chamber at 31.5 °C. Animals were administered 10.4–11.8 MBq 4-[18F]fluoroglutamine via intravenous injection and imaged using a scanner. During imaging, animals were maintained under 2% isoflurane anesthesia in oxygen at 2 L/min and kept warm for the duration of the PET scan. PET images in xenograft-bearing mice were acquired as 60-minute dynamic data sets. Imaging was initiated three hours post-treatment following vehicle or V-9302 (75 mg/kg) administration. PET data were reconstructed using a three-dimensional (3D) ordered subset expectation maximization/maximum a posteriori (OSEM3D/MAP) algorithm. The resulting three-dimensional reconstructions had an x-y voxel size of 0.474 mm and inter-slice distance of 0.796 mm. ASIPro software was used to manually draw 3D regions of interest (ROIs) surrounding the entire tumor volume. 4-[18F]fluoroglutamine uptake was quantified as the percentage of the injected dose per gram of tissue (%ID/g). Significance was calculated using a t-test in Graphpad Prism. Error is reported as standard deviation (SD). |
| Molecular Weight | 538.68 |
| Formula | C34H38N2O4 |
| Cas No. | 1855871-76-9 |
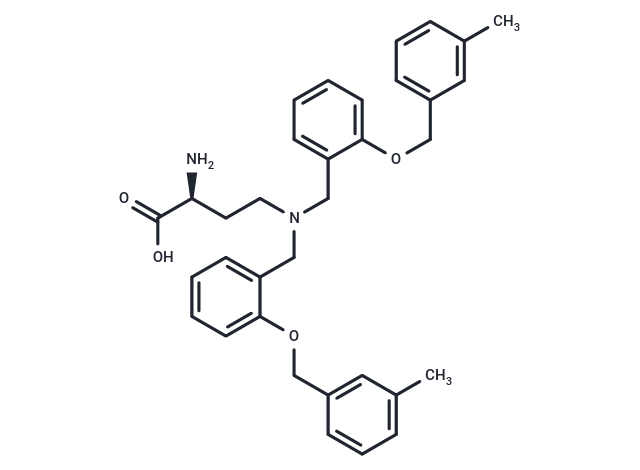
| Smiles | Cc1cccc(COc2ccccc2CN(CC[C@H](N)C(O)=O)Cc2ccccc2OCc2cccc(C)c2)c1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.179 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | store at low temperature,keep away from moisture | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: Insoluble DMSO: 11 mg/mL (20.42 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 10 mg/mL (18.56 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.