Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Thiamine hydrochloride (Vitamin B1) is an essential micronutrient and a cofactor for many central metabolic enzymes.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $33 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $42 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 g | $59 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Thiamine hydrochloride (Vitamin B1) is an essential micronutrient and a cofactor for many central metabolic enzymes. |
| Targets&IC50 | Neuroblastoma:5.4 mM, Hypo19/7:12.5 µM, pancreatic:4.9 mM |
| In vitro | METHODS: SK-N-BE cells (neuroblastoma cells) and Panc-1 cells (pancreatic cancer cells) were treated with Thiamine hydrochloride (10-5-102 mM) for 5 days, and the cell growth inhibition was detected by crystal violet assay. RESULTS: Thiamine hydrochloride inhibited the growth of SK-N-BE cells (IC50=4.9 mM) and Panc-1 cells (IC50=5.4 mM). [1] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To investigate the effect of Thiamine hydrochloride on memory, Thiamine hydrochloride (300 µg/kg) was administered to adult mice with scopolamine-induced memory dysfunction every other day for the last 14 days of the experiment. RESULTS: Thiamine hydrochloride improved memory dysfunction in mice through Nrf-2/TLR4 signaling pathway. [2] METHODS: To study the anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperalgesia effects of Thiamine hydrochloride, Thiamine hydrochloride (150-200 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to Wistar rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis for 21 days. RESULTS: Thiamine hydrochloride showed anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperalgesia effects. [3] METHODS: To study the anti-inflammatory activity of Thiamine hydrochloride, Thiamine hydrochloride (20 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to rats with colitis for 5 days. RESULTS: Thiamine hydrochloride attenuated macroscopic parameters and the summary colitis index in colitis rats. [4] |
| Synonyms | Vitamin B1 hydrochloride, Thiamine HCl, Thiamine chloride hydrochloride |
| Molecular Weight | 337.27 |
| Formula | C12H18Cl2N4OS |
| Cas No. | 67-03-8 |
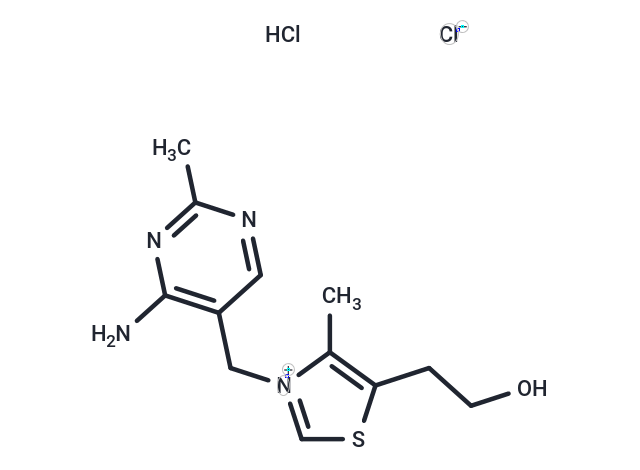
| Smiles | Cl.[Cl-].CC1=C(CCO)SC=[N+]1CC1=C(N)N=C(C)N=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.401 g/cm3 |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | keep away from moisture | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 95 mg/mL (281.67 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 3.37 mg/mL (9.99 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.