Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
RAGE antagonist peptide acetate is an advanced antagonist of glycation end products (RAGE). RAGE antagonist peptide acetate possesses anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory activities. RAGE antagonist peptide acetate prevents RAGE from binding with several of its most important ligands, including HMGB-1, S100P, and S100A4.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $85 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $248 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $372 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $626 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $892 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $1,220 | - | In Stock |
| Description | RAGE antagonist peptide acetate is an advanced antagonist of glycation end products (RAGE). RAGE antagonist peptide acetate possesses anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory activities. RAGE antagonist peptide acetate prevents RAGE from binding with several of its most important ligands, including HMGB-1, S100P, and S100A4. |
| In vitro | In cancer cells, RAGE antagonist peptide acetate reduces the ability of the ligands to stimulate RAGE activation of NFκB[2]. |
| In vivo | In mice bearing asthma, RAGE antagonist peptide acetate (RAP; 4 mg/kg; i.p.) blunts airway reactivity, airway inflammation and goblet cell metaplasia, and decreases release of Th2 cytokines. RAGE antagonist peptide acetate also reduces total, cytoplasmic and nuclear levels of β-catenin, enhanced β-catenin phosphorylation at Ser33/37/Thr41, which triggers ubiquitination, down-regulated expression of β-catenin targeted genes, and tends to keep β-catenin at the cytomembrane, shifting β-catenin from a signalling active pattern to an adhesive function[1]. RAGE antagonist peptide acetate reduces the growth and metastasis of pancreatic tumors and also inhibited glioma tumor growth. RAGE antagonist peptide acetate (100 μg) inhibits RAGE-mediated Basal NFκB Activity in PDAC cells in vivo[2]. |
| Molecular Weight | 1332.61 |
| Formula | C59H105N13O19S |
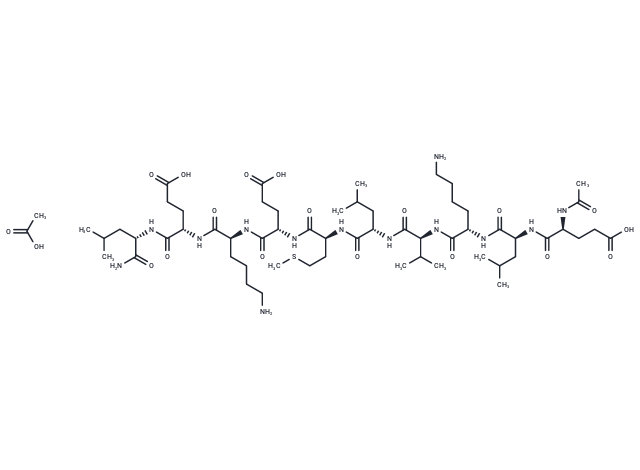
| Smiles | CC(O)=O.CSCC[C@@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(N)=O)CC(C)C)=O)CCC(O)=O)=O)CCCCN)=O)CCC(O)=O)=O)NC([C@@H](NC([C@H](C(C)C)NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC(C)=O)CCC(O)=O)=O)CC(C)C)=O)CCCCN)=O)=O)CC(C)C)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.31g/cm3 |
| Sequence | Glu-Leu-Lys-Val-Leu-Met-Glu-Lys-Glu-Leu |
| Sequence Short | ELKVLMEKEL |
| Storage | keep away from moisture | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.