Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
The P7C3 class of neuroprotective aminopropyl carbazoles has been shown to block neuronal cell death in models of neurodegeneration. We now show that P7C3 molecules additionally preserve axonal integrity after injury, before neuronal cell death occurs, in a rodent model of blast-mediated traumatic brain injury (TBI). This protective quality may be linked to the ability of P7C3 molecules to activate nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase, the rate-limiting enzyme in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide salvage.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $43 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $70 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $133 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $239 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $397 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $48 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | The P7C3 class of neuroprotective aminopropyl carbazoles has been shown to block neuronal cell death in models of neurodegeneration. We now show that P7C3 molecules additionally preserve axonal integrity after injury, before neuronal cell death occurs, in a rodent model of blast-mediated traumatic brain injury (TBI). This protective quality may be linked to the ability of P7C3 molecules to activate nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase, the rate-limiting enzyme in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide salvage. |
| In vitro | In U2OS Cells, P7C3 protects cells from doxorubicin-mediated toxicity, and enhances the flux of nicotinamide through the NAMPT-mediated salvage pathway. [1] |
| In vivo | In mouse brain, P7C3 (40 mg/kg, p.o.) induces neurogenesis and enhances survival of newborn neurons. In npas3?/? mice, P7C3 (20 mg/kg/d, p.o.) increases the magnitude of neural precursor cell proliferation, and corrects morphological and electrophysiological deficits. [2] In the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down Syndrome, P7C3 restores hippocampal neurogenesis though a significant increase in total Ki67+, DCX+, and surviving BrdU+ cells. [3] |
| Kinase Assay | To assess the effect of compounds on auto-PARsylation of TNKS, 1 μM GST fusion protein containing the SAM domain and the PARP domain of TNKS2 (a.a. 872-1166) is mixed with 5 μM biotin-NAD+ and 2 μM XAV939 or LDW643 at 30°C for 2.5 hours. Samples are resolved by SDS-PAGE and probed with streptavidin AlexaFluor680. To assess PARsylation of axin, recombinant full-length TNKS2 (expressed/purified as a N-terminal His-tagged protein in bacteria) is incubated with GST-axin 1 (1-280) in the presence of biotin-NAD+ with or without XAV939. The products are resolved and probed with Streptavidin-HRP and imaged using a AlphaInnotech imager. To assess the effect of XAV939, IWR-1-enod, IWR-1-exo, and ABT-888 on auto-PARsylation of TNKS2, His-tagged full-length TNKS2 is incubated with 5 μM biotin-NAD+ and 3 mM of indicated compounds. The products are resolved and probed with Streptavidin-HRP. LC/MS-based high throughput auto-PARsylation assays for PARP1, PARP2, TNKS1, and TNKS2 are setup to monitor the formation of nicotinamide (a by-product of the PARsylation reaction) in the presence of small molecule inhibitors. |
| Molecular Weight | 474.19 |
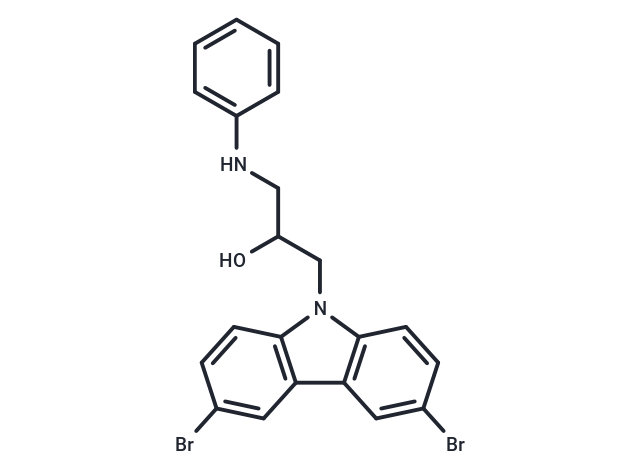
| Formula | C21H18Br2N2O |
| Cas No. | 301353-96-8 |
| Smiles | OC(CNc1ccccc1)Cn1c2ccc(Br)cc2c2cc(Br)ccc12 |
| Relative Density. | 1.61 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 16 mg/mL (33.74 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 80 mg/mL (168.71 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 3.3 mg/mL (6.96 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.