Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Isomazole is a novel orally available phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor with calcium-sensitizing properties that inhibits PDE3 and PDE4.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $146 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $350 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $530 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $859 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $1,180 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $1,590 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $3,190 | In Stock |
| Description | Isomazole is a novel orally available phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor with calcium-sensitizing properties that inhibits PDE3 and PDE4. |
| In vivo | Isomazole (10 and 20 micrograms/kg/min; ) to 10 awake dogs with right-sided congestive heart failure produced by pulmonary artery constriction and tricuspid valve avulsion found that increased cardiac output, heart rate, right ventricular and left ventricular (LV) dP/dt, LVdP/dt/P and decreased aortic pressure and total peripheral vascular resistance. Simultaneously, blood flow increased to myocardium, quadriceps muscle, brain and splanchnic beds, whereas vascular resistance decreased. Furthermore, Isomazole increased LV oxygen consumption and decreased trans-coronary arteriovenous oxygen difference. Angiotensin II was infused to restore mean aortic pressure to base-line values during Isomazole infusion; however, despite the return of aortic pressure to base-line values, cardiac output, LVdP/dt, and LVdP/dt/P remained elevated. The systemic and regional hemodynamic effects of Isomazole were unaffected by pretreatment with propranolol and mecamylamine. Thus, Isomazole exerted positive inotropic, chronotropic, and vasodilator effects in congestive heart failure dogs. The inotropic effect of Isomazole was independent of the decrease in aortic pressure, and the hemodynamic effects of Isomazole were not mediated via the autonomic nervous system. Furthermore, the decrease in trans-coronary arteriovenous oxygen difference suggests that Isomazole exerted an active coronary vasodilator action which may improve the myocardial oxygen demand/supply ratio.[2] |
| Molecular Weight | 287.34 |
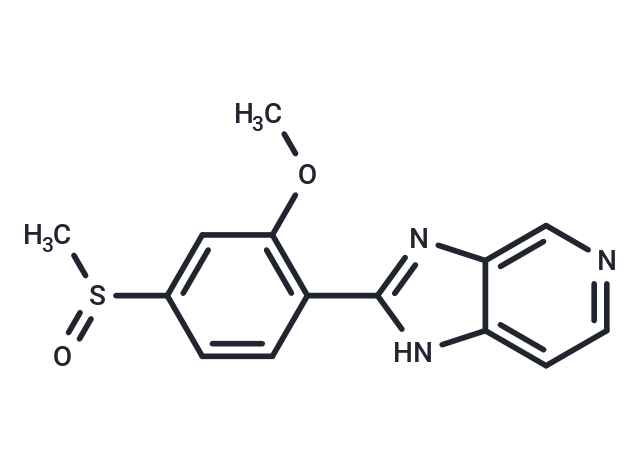
| Formula | C14H13N3O2S |
| Cas No. | 86315-52-8 |
| Smiles | O(C)C1=C(C=CC(S(C)=O)=C1)C=2NC=3C(N2)=CN=CC3 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 60 mg/mL (208.81 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.