Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
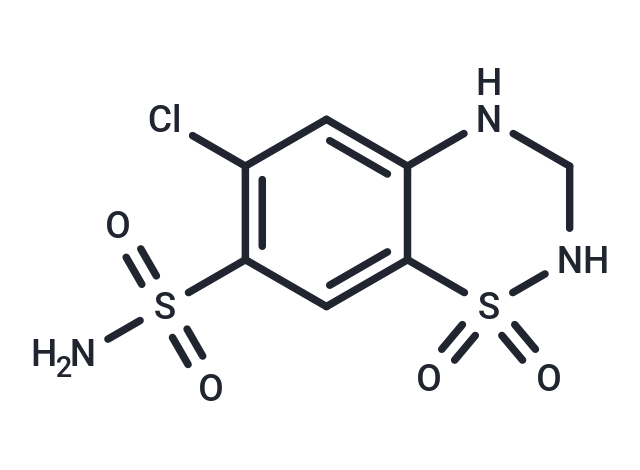
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) is a Thiazide Diuretic. The physiologic effect of hydrochlorothiazide is by means of Increased Diuresis.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) is a Thiazide Diuretic. The physiologic effect of hydrochlorothiazide is by means of Increased Diuresis. |
| Kinase Assay | Kinase autophosphorylation assays: Kinase assays using wild-type and mutant glutathione S-transferase (GST)-Abl fusion proteins (c-Abl amino acids 220-498) are done. GST-Abl fusion proteins are released from glutathione-Sepharose beads before use; the concentration of ATP is 5 μM. Immediately before use in kinase autophosphorylation and in vitro peptide substrate phosphorylation assays, GST-Abl kinase domain fusion proteins are treated with LAR tyrosine phosphatase. After 1-hour incubation at 30 °C, LAR phosphatase is inactivated by addition of sodium vanadate (1 mM). Immunoblot analysis comparing untreated GST-Abl kinase to dephosphorylated GST-Abl kinase is routinely done using phosphotyrosine-specific antibody 4 g10 to confirm complete (>95%) dephosphorylation of tyrosine residues and c-Abl antibody CST 2862 to confirm equal loading of GST-Abl kinase. The Dasatinib concentration range is extended to 1,000 nM for mutant T315I. These same inhibitor concentrations are used for the in vitro peptide substrate phosphorylation assays. The three inhibitors are tested over these same concentration ranges against GST-Src kinase and GST-Lyn kinase. |
| Synonyms | HCTZ |
| Molecular Weight | 297.74 |
| Formula | C7H8ClN3O4S2 |
| Cas No. | 58-93-5 |
| Smiles | NS(=O)(=O)C1=C(Cl)C=C2NCNS(=O)(=O)C2=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.6761 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 65 mg/mL (218.31 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (6.72 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.