Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Histamine Phosphate (Histamine acid phosphate) acts directly on the blood vessels to dilate arteries and capillaries mediated by both H 1- and H 2-receptors.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $48 | Backorder |
| Description | Histamine Phosphate (Histamine acid phosphate) acts directly on the blood vessels to dilate arteries and capillaries mediated by both H 1- and H 2-receptors. |
| In vitro | Histamine (10 μM) gives a larger inositol monophosphate accumulation in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Histamine (10 μM) stimulates the level of radioactivity into the InsP3-containing fraction in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Histamine (100 μM) stimulates incorporation into the InsP3-containing eluate in a less extent than for angiotensin I1 and bradykinin. [1] |
| In vivo | Histamine phosphate (0.025 mg/kg) produces a mean increase in basilar blood flow of 145% of control in dogs. Histamine phosphate produces considerable increases in basilar blood flow as well as a decrease in femoral arterial blood pressure in dogs when injected intravenously and measured with an electromagnetic flow transducer. [2] Histamine phosphate (4 μg/kg) causes lymph flow to increase from 6.0 to 27.0 (SEM) ml/h in unanesthetized sheep. Histamine phosphate (4 μg/kg) also causes increases in lung water, pulmonary vascular resistance, arterial PCO2, pH, and hematocrit, and decreases in cardiac output and arterial PO2 in unanesthetized sheep. [3] Histamine phosphate (8.3 mg/kg/min) causes no significant change in pulmonary lymph flow (QL) or protein concentration (CL) in anesthetized open-chested dogs, however, both are increased after alloxan. Histamine phosphate (8.3 mg/kg/min) also causes no significant change in the pulmonary capillary membrane filtration coefficient (Kf) and the maximum capillary pressure (PCcritical) in anesthetized open-chested dogs. [4] Histamine phosphate (50 mg/kg) produces a pronounced rise in acid secretion but the output of pepsin remained unchanged in the unanaesthetized intact rat. Histamine phosphate (50 mg/kg) produces maximal stimulation of gastric acid secretion and is free from toxic effects in the unanaesthetized intact rat. [5] |
| Alias | Histamine diphosphate, Histamine acid phosphate |
| Molecular Weight | 307.14 |
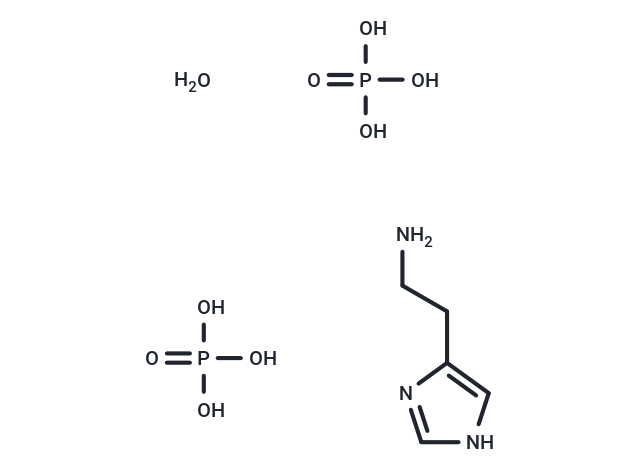
| Formula | C5H9N·2H3O4P |
| Cas No. | 51-74-1 |
| Smiles | O.OP(O)(O)=O.OP(O)(O)=O.NCCc1c[nH]cn1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 10 mM, Sonication is recommended. DMSO: Insoluble | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.