 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Forskolin (Coleonol) is a natural product, an adenylate cyclase activator (EC50=0.5 μM). Forskolin increases cAMP levels, activates PXR and FXR, and induces autophagy. Forskolin produces positive inotropic effects in the heart, and has platelet anticoagulant and antihypertensive effects.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $36 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $51 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $78 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $97 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $147 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $192 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $323 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $51 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Forskolin (Coleonol) is a natural product, an adenylate cyclase activator (EC50=0.5 μM). Forskolin increases cAMP levels, activates PXR and FXR, and induces autophagy. Forskolin produces positive inotropic effects in the heart, and has platelet anticoagulant and antihypertensive effects. |
| Targets&IC50 | Adenylyl cyclase:0.5 μM (cell free), adenylyl cyclase (type I):0.5 μM (EC50), MCF-7 cells:63.3 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Rat adrenal medullary chromosomal tumor cells PC12 were treated with Forskolin (0.01-10 µM) for 3-48 h. The growth inhibition of the cells was detected by MTT. RESULTS: The cell viability decreased rapidly after treatment with 10 µM Forskolin (88.4% after 6 h and 60.5% after 48 h). [1] METHODS: Human myeloma cells U266, H929, INA-6, RPMI 8226 and OPM-2 were treated with Forskolin (1-100 µM) for 72 h. Cell death was detected by Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: Forskolin dose-dependently induced cell death in human myeloma cells, with U266, OPM-2 and INA-6 being more sensitive than H929 and RPMI 8226 cells. [2] METHODS: Human IL-2-dependent leukemia cells Kit 225 and human leukemia cells MT-2 were treated with Forskolin (1-100 μM) for 20 min, and cAMP concentration was measured by ELISA. RESULTS: Forskolin induced an up-regulation of cAMP levels, which reached a maximum level between 50-100 μm. [3] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To assay anti-tumor activity in vivo, Forskolin (4-5 mg/kg in PBS/DMSO solution (15:1)) was injected intraperitoneally into BALB/c nude mice bearing murine multiple myeloma tumor MOPC315, and was administered on the 2nd/4th/6th day after tumor cell injection. RESULTS: All mice eventually developed tumors, but Forskolin significantly delayed tumor growth in vivo. Compounds that increase cAMP may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of multiple myeloma. [4] METHODS: To investigate the effect of Forskolin on retinal inflammation under diabetic conditions, Forskolin (50 mg/kg) was administered by gavage once weekly for twelve weeks to C57BL/6 mice in the STZ-induced diabetes model. RESULTS: Retinal glucose concentrations were increased in both diabetic control and Forskolin-treated groups compared to normal controls, but due to down-regulation of glucose transporter protein 1 expression, the Forskolin-treated group was only about 68.06% of the diabetic control group. ICAM-1 and TNF-α expression was up-regulated in the Forskolin-treated and diabetic control groups compared to the normal control group, but the expression levels of these two inflammatory factors in the Forskolin-treated group were 68.75% and 75.37% of those in the diabetic control group, respectively. [5] |
| Kinase Assay | For Jak3 kinase assays, Fsk-treated MT-2 cells were lysed, clarified, and immunoprecipitated using Jak3 antibody as described above. Kinase reactions were carried out as described previously at 30 °C for 20 min. For PKA kinase assays, untreated MT-2 cells were lysed, and Jak3 was immunoprecipitated and bound to PAS beads as described previously. Immunoprecipitated Jak3 was washed with kinase buffer (50 mM Hepes-NaOH (pH 7.4), 10 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM EGTA, 0.5 mM DTT, 20 μg/ml aprotinin, 10 μg/ml leupeptin, 1 μg/ml pepstatin A) and incubated with 200 μM ATP and purified protein kinase A catalytic subunit (PKAc) as indicated in the figure legends. Kinase reactions were carried out at 32 °C for 30 min followed by vigorous washing of the beads with cold kinase wash buffer as described previously. For [γ-32P]ATP radiolabeled kinase assays using recombinant Jak3, Hek293 cells were transfected with wild type (WT) Jak3 or kinase-dead Jak3 K855A using Lipofectamine 2000 according to the manufacturer's instructions. Cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with Jak3 antibody. Jak3-bound PAS beads were washed three times in cold lysis buffer followed by kinase buffer. Kinase reactions were initiated by adding 10 μCi [γ-32P]ATP, 10 μm unlabeled ATP, and 1 μg of purified PKAc to Jak3-bound PAS bead reaction mixtures. Kinase reactions were performed at 32 °C for 30 min. Jak3-bound PAS beads were washed three times in radioimmunoassay buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 75 mM NaCl, 20 mM EDTA, 10 mM EGTA, 20 mM Na4P2O7, 50 mM NaF, 20 mM 2-glycerolphosphate, 1 mM p-nitrophenyl phosphate, 0.1% Triton X-100) and one time in kinase wash buffer. The reactions were stopped by adding 2× SDS-PAGE sample buffer followed by SDS-PAGE. Coomassie stainable Jak3 bands were excised from the PVDF membrane and subjected to phosphoamino acid analysis [2]. |
| Cell Research | Kit 225 or MT-2 cells were treated with 1, 5, 10, 20, 50, or 100 μM Forskolin for 20 min at 37 °C. Cells were lysed and clarified by centrifugation, and the concentration of cAMP was detected by direct cAMP ELISA. Optical density was measured at 405 nm, and the concentration of intracellular cAMP was calculated using a weighted four parameter logistic curve according to the manufactures instructions [2]. |
| Animal Research | Forskolin was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and injected intraperitoneally into neonatal mice at postnatal days 4 (P4) and 5 (P5). Mice injected with DMSO served as the controls. The treated mice were euthanized at P6, and their retinas were isolated for whole-mount immunohistochemistry (IHC). We first tested the effect of different concentrations of forskolin on the survival rate and retinal vasculature and determined the optimal concentration, 1.0 μg/50 μL (0.3 mg/kg) at P4 and 1.5 μg/50 μL (0.5 mg/kg) at P5, used to compare the retinal vascular phenotypes between WT mice and Mrp4-deficient mice [4]. . After acclimatization for 2 weeks, animals were randomly divided into four groups of eight rats each and treated for six consecutive weeks as follows: The first group was treated with CCl4 (50% CCl4/corn oil; 0.5 mL·kg?1, i.p.) twice a week to induce liver fibrosis. The second group was given forskolin only at a dose of 10 mg·kg?1, i.p., dissolved in a DMSO/saline solution (1:49) five times a week. The third group was given both CCl4 and forskolin. The dose of forskolin used here was based on the results of our preliminary study. The fourth group served as the normal control, receiving vehicles only. At 24 h after the last injection, blood samples were collected from the retro‐orbital plexus after light anesthesia with sodium pentobarbital (50 mg·kg?1, i.p.). Serum was separated by centrifugation at 3000× g for 10 min and was used for the assessment of liver functions. Rats were killed by cervical dislocation, and livers were removed and weighed. A portion of liver tissue was washed and homogenized to obtain a 20% (w·v?1) homogenate, which was used for assessment of oxidative stress, inflammatory and fibrogenic markers. Another portion was placed in formalin for immunohistochemical and histopathological analyses. The remainder was stored at ?80°C, together with the 20% homogenate, until needed [5]. |
| Synonyms | FSK, Colforsin, Coleonol |
| Molecular Weight | 410.50 |
| Formula | C22H34O7 |
| Cas No. | 66575-29-9 |
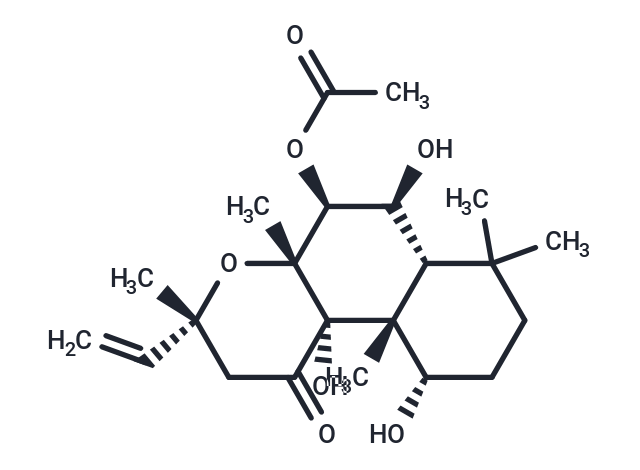
| Smiles | CC(=O)O[C@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2C(C)(C)CC[C@H](O)[C@]2(C)[C@@]2(O)C(=O)C[C@@](C)(O[C@]12C)C=C |
| Relative Density. | 1.23 g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,keep away from moisture,store at low temperature | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: Insoluble DMSO: 245.00 mg/mL (596.83 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 15.00 mg/mL (36.54 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 3.00 mg/mL (7.31 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.