 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

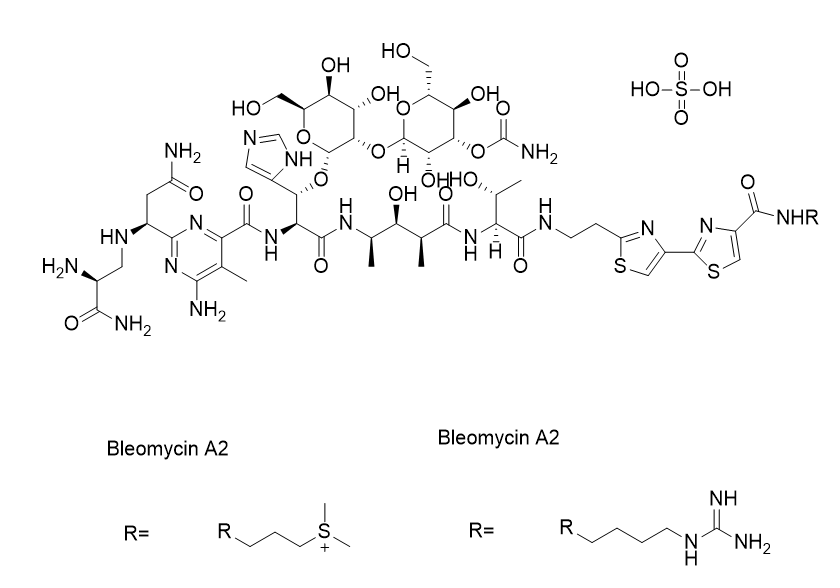
Bleomycin sulfate is a glycopeptide antibiotic with antitumor activity. It is commonly used as a DNA-damaging agent and DNA synthesis inhibitor. It functions by inducing DNA strand breaks without affecting RNA strands. Bleomycin sulfate is widely used in cancer research and for establishing pulmonary fibrosis animal models.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $37 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $50 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $74 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $123 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $270 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $395 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $498 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $725 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Bleomycin sulfate is a glycopeptide antibiotic with antitumor activity. It is commonly used as a DNA-damaging agent and DNA synthesis inhibitor. It functions by inducing DNA strand breaks without affecting RNA strands. Bleomycin sulfate is widely used in cancer research and for establishing pulmonary fibrosis animal models. |
| Targets&IC50 | MIAPaCa2 cells:5.9/6.4/2.6 μM (24/48/72 h), UT-SCC-19A cells:4 nM, UT-SCC-12A cells:14.2 ± 2.8 nM, UT-SCC-12B cells:13.0 ± 1.1 nM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human pancreatic cells (PCCs) AsPC-1 and MIA PaCa-2 were treated with Bleomycin Sulfate (0.1-100 µM) for 24-72 h. Cell growth inhibition was detected by MTT. RESULTS: AsPC-1 cells did not respond to Bleomycin Sulfate, and Bleomycin Sulfate significantly inhibited the cell growth of MIA-PaCa-2, with IC50s of 5.9/6.4/2.6 μM at 24/48/72 h treatment, respectively.[1] METHODS: MSCs were treated with Bleomycin Sulfate (1800 ng/mL) for 24-96 h. Sub-G1 and caspase-3 were detected by Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: Bleomycin Sulfate induced the up-regulation of sub-G1 and caspase-3 activation, indicating that Bleomycin Sulfate induced apoptosis. [2] METHODS: Normal rat alveolar macrophages were incubated with Bleomycin Sulfate (0.01-1 μg/mL) for 18 h, and MDGF levels were determined using the MDGF Assay. RESULTS: Bleomycin Sulfate stimulated the production of fibroblast growth factor (MDGF) in macrophages. [3] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To assay antitumor activity in vivo, Bleomycin Sulfate (20 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally five times every two days to BALB/c mice bearing mouse colorectal carcinoma tumor CT26 shControl or shCRT. RESULTS: Bleomycin Sulfate delayed the growth of control shRNA-transfected CT26 cells, but had no effect on CRT shRNA-transfected CT26 cells. [4] METHODS: To study the time course of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice, Bleomycin Sulfate (0.06 mg/only in 0.9% saline) was administered to C57Bl/6J mice by a single intratracheal instillation (IT). RESULTS: Bleomycin Sulfate induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. The most appropriate time point for assessing lung fibrosis in this model is 14 days after IT titration of Bleomycin Sulfate, which is based on the observation that animals show extensive fibrosis at 14 days, but less variability in the fibrotic response and lower mortality than at 21 days. [5] |
| Disease Modeling Protocol | Pulmonary fibrosis model
*Precautions: All mice were sacrificed 14 days after modeling (day 14). Establishment of pulmonary fibrosis model
*Precautions: All mice were sacrificed 14 days after modeling (on day 14). |
| Cell Research | ADIPO-P2 cells are grown in D-MEM high glucose medium supplemented with 20% fetal calf serum, penicillin (100 U/mL) and streptomycin (100 μg/mL) at 37 °C and 5% CO2 atmosphere. Cells are cultured as monolayer in TC25 Corning flasks containing 1.5 × 105 cells/mL. For each experiment, two flasks are set up, one for the control and one for the treated culture. During the log phase of growth ADIPO-P2 cells are treated with a 30 minutes pulse of 2.5 μg/mL of Bleomycin sulfate. Control cultures are set up in parallel but not exposed to Bleomycin sulfate. Time of exposure and concentration of Bleomycin sulfate are chosen according to previous studies carried out in our laboratory with mammalian cells exposed to Bleomycin sulfate. At the end of the pulse treatment with Bleomycin sulfate, the cells are washed twice with Hank's balanced salt solution and kept in culture with fresh culture medium until harvesting. Cells are continuously maintained in culture during 5 passages or subcultures after treatment. Subcultivation is carried out whenever the cultures became confluent (approximately 4 × 105 cells/mL of culture medium). To estimate cell growth, at the time of subcultivation cells are collected by trypsinization, an aliquot of about 200 μL stained with 0.4% trypan blue, and the number of viable cells is determined. Cells are then suspended in fresh culture medium and dispensed into new culture flasks containing 1 × 105 cells/mL to continue growing. The rest of the cells is discarded or dispensed in another flask for cytogenetic analysis, which is performed at 18 hours and 10 days after the end of treatments. To analyze chromosomal aberrations, colchicine (0.1 μg/mL) is added to cell cultures during the last 3 hours of culture. Chromosome preparations are made following standard procedures. After harvesting, cells are hypotonically shocked, fixed in methanol:acetic acid (3:1), spread onto glass slides and processed for PNA-FISH.Two independent experiments are carried out. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | NSC125066, Blenoxane |
| Molecular Weight | 1523 (average) |
| Formula | C55H84N17O21S3 |
| Cas No. | 9041-93-4 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | keep away from moisture,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) H2O: 92 mg/mL, Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 262.5 mg/mL, Sonication is recommended. |
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 5 mg/mL, Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.