Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

AEBSF hydrochloride (Pefabloc SC) is an irreversible inhibitor of serine proteases, such as chymotrypsin, kallikrein, thrombin, plasmin, and trypsin.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $43 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $51 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $92 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | AEBSF hydrochloride (Pefabloc SC) is an irreversible inhibitor of serine proteases, such as chymotrypsin, kallikrein, thrombin, plasmin, and trypsin. |
| In vitro | In a mouse model of cockroach allergen-induced asthma, AEBSF was able to mitigate respiratory reactions and potential inflammation. Intraperitoneal injection of 76.8 mg/kg AEBSF daily in mice lethally inoculated with Toxoplasma gondii extended their survival period. |
| In vivo | AEBSF is a serine protease inhibitor that suppresses the lysis of leukemia cells by macrophages without inhibiting the secretion of TNF-α and IL-1β by these cells. In five different human cell lines, AEBSF inhibits the formation of amyloid-beta (Aβ) by blocking the secretion of both neural and non-neural β-secretase products. Additionally, AEBSF disrupts embryonic growth within the endometrium and modifies protein secretion mechanisms to prevent the adhesion of HeLa cells in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. |
| Cell Research | The HeLa cells suspended in RPMI-1640 media containing 10% FCS are plated into each well of a 96-well microplate (5×103 cells/200 μL/well). After incubation for 24 h at 37°C, cells are treated with different doses of AEBSF (0, 25, 50, 100 μg/mL) for 48 h. Then, 20 μL fresh 3-(4,5)-dimethylthiahiazo (-z-y1)-3,5-diphenytetrazoliumromide (MTT) reagent (5 μg/μL) is added into each well, and cells are cultured at 37°C in 5% CO2 for another 4 h. The media are discarded carefully, and 150 μL DMSO is added. Absorbance is read on a microplate reader at dual wavelengths of 540 and 620 nm. |
| Alias | Pefabloc SC, AEBSF HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 239.69 |
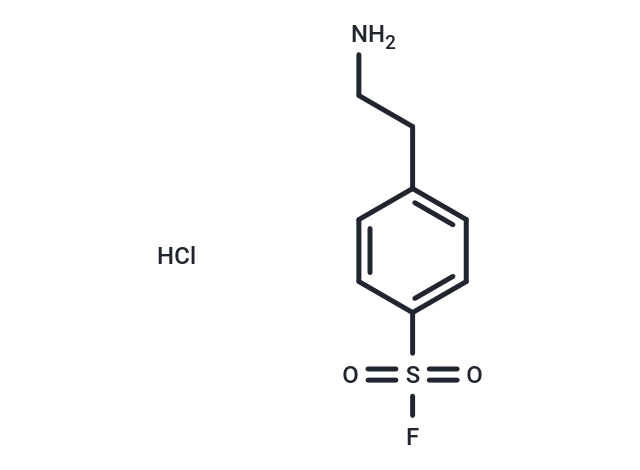
| Formula | C8H11ClFNO2S |
| Cas No. | 30827-99-7 |
| Smiles | Cl.NCCc1ccc(cc1)S(F)(=O)=O |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 24 mg/mL (100.13 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 60 mg/mL (250.32 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.