 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

2-Aminopurine is a double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase, protein kinase R (PKR) inhibitor.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $39 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock | In Stock |

| Description | 2-Aminopurine is a double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase, protein kinase R (PKR) inhibitor. |
| In vitro | 1. DNA structure detection using 2-aminopurine 1. Solution configuration: 2-Aminopurine is usually used at a concentration of 0.1–50 μM, depending on the experimental requirements and the sensitivity of the fluorescence signal. 2. Material preparation: 1) 2-aminopurine labeled oligonucleotides: 2-AP is inserted into a specific DNA sequence by solid phase synthesis. 2) DNA sample: Oligonucleotides containing 2-AP, which can be single-stranded or double-stranded after hybridization with a complementary strand. 3) Fluorescence spectrometer: A device that can detect fluorescence emission and attenuation, usually with an excitation wavelength in the range of 310-320 nm and an emission wavelength in the range of 370-380 nm. 3. Steps: 1) Oligonucleotide synthesis: 2-AP is inserted into a predetermined position in the DNA sequence during the synthesis process. 2) Sample preparation: Prepare a 2-AP labeled DNA solution, and the concentration should be adjusted according to the experimental needs. 3) Fluorescence measurement: Under an excitation wavelength of 310-320 nm, measure the fluorescence intensity and decay (emission wavelength 370-380 nm). 4) Fluorescence decay analysis: Analyze the fluorescence decay curve to explore the stacking, conformational changes and interactions of DNA with other molecules (such as proteins or ligands). 2. Detection of DNA conformational changes and binding interactions 1. Material preparation: (1) 2-AP labeled oligonucleotides: Used to study the structural changes of DNA. (2) Binding ligand/protein: DNA binding protein, small molecule ligand or other DNA interaction molecules. (3) Fluorescence spectrometer: Used to detect fluorescence signals at appropriate wavelengths. 2. Steps: (1) DNA-protein binding: Incubate 2-AP labeled DNA with DNA binding protein or ligand. (2) Fluorescence measurement: Observe the changes in fluorescence intensity and decay after binding or conformational changes. (3) Data analysis: Determine the kinetics of ligand binding, DNA structural transitions and DNA-protein or ligand interactions through fluorescence changes. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Molecular Weight | 135.13 |
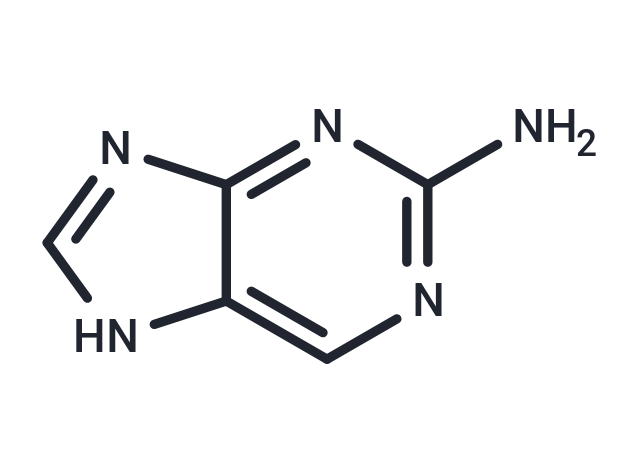
| Formula | C5H5N5 |
| Cas No. | 452-06-2 |
| Smiles | NC1=NC=C2NC=NC2=N1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.612 g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 10 mg/mL (74 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.