 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Mycophenolic acid sodium is a potent uncompetitive inhibitor of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) with an EC50 of 0.24 μM, exhibiting broad antiviral activity against RNA viruses, including influenza, along with immunosuppressive properties and antiangiogenic and antitumor effects [1][2].
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $2,140 | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 weeks | |
| 50 mg | $2,785 | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 weeks | |
| 100 mg | $3,520 | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 weeks |
| Description | Mycophenolic acid sodium is a potent uncompetitive inhibitor of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) with an EC50 of 0.24 μM, exhibiting broad antiviral activity against RNA viruses, including influenza, along with immunosuppressive properties and antiangiogenic and antitumor effects [1][2]. |
| In vitro | Mycophenolic acid sodium has been demonstrated to possess antiviral properties against an array of RNA viruses, including influenza, dengue virus, Zika virus, rotavirus, CCHFV, and hantavirus [1]. It targets IMPDH, a crucial enzyme in guanosine nucleotides' de novo synthesis [2]. When tested at concentrations ranging from 0.01 to 1 μM over 72 hours, mycophenolic acid sodium displayed a selective inhibitory effect on the proliferation of endothelial cells and fibroblasts, with endothelial cells being more susceptible (IC 50 <500 nM) to its antimitotic effects [2]. In contrast, fibroblasts showed a higher tolerance (IC 50 <1 μM). Among human tumor cell lines tested, A549 non-small cell lung cancer and PC3 prostate cancer cells manifested moderate sensitivity (IC 50 >1 μM), whereas U87 glioblastoma cells were resistant to up to 1 μM of mycophenolic acid sodium treatment [2]. Furthermore, a dose-dependent modulation of HDAC2 and MYC (down-regulation) and NDRG1 (up-regulation) was observed with mycophenolic acid sodium treatment (0.05-2 μM; 18 hours) [2]. In cell proliferation assays, primary isolated human dermal microvascular endothelial cells and fibroblasts were preferentially inhibited by the treatment, contrasting with U87 glioblastoma cells' resistance and the intermediate sensitivity of A549 and PC3 cancer cells [2]. Western Blot analysis further confirmed the dose-dependent regulatory effect of mycophenolic acid sodium on HDAC2, MYC, and NDRG1 in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells, providing a detailed understanding of its mechanism [2]. |
| In vivo | Mycophenolic acid (120 mg/kg; oral gavage; b.i.d.) exhibits potent anti-tumor activity by altering the tumor microenvironment and significantly inhibiting U87 tumor growth in BALB/c nude mice [2]. Using an athymic 8-week-old, 20 g BALB/c nu/nu mouse model with a Mycophenolic acid-resistant U87 tumor, 120 mg/kg of MMF (the morpholinoethyl ester prodrug of Mycophenolic acid) was administered orally twice daily. After 14 days post-tumor implantation, the MMF-treated group showed a 70% reduction in tumor growth compared to controls. Furthermore, MMF treatment significantly decreased microvessel density (by 44%) and pericyte coverage (by 78%), as indicated by CD31 and α-smooth muscle actin staining, respectively, suggesting impaired tumor vascularization and underscoring its efficacy against tumor proliferation [2]. |
| Molecular Weight | 342.323 |
| Formula | C17H19NaO6 |
| Cas No. | 37415-62-6 |
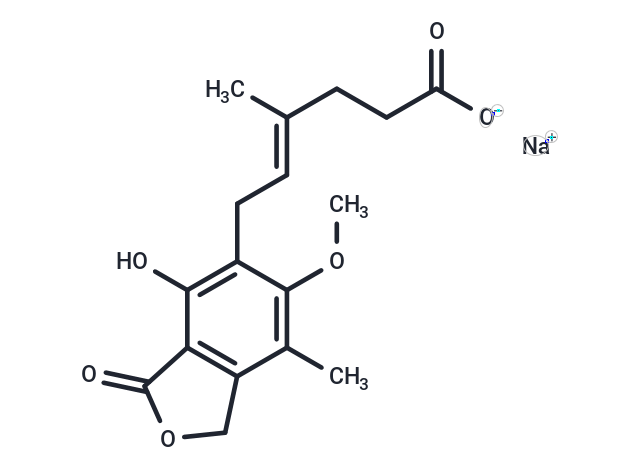
| Smiles | [Na+].COc1c(C)c2COC(=O)c2c(O)c1C\C=C(/C)CCC([O-])=O |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.