 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Arachidonic acid (Immunocytophyt) is a polyunsaturated omega-6 essential fatty acid that serves as a major component of biological membranes and animal phospholipids. It is synthesized from dietary linoleic acid and acts as a precursor to lipid mediators such as prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Arachidonic acid can improve cognitive responses and cardiovascular function and is commonly used to induce paw edema models.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $39 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $55 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $77 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $97 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $122 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $178 | - | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $297 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $43 | - | In Stock |

| Description | Arachidonic acid (Immunocytophyt) is a polyunsaturated omega-6 essential fatty acid that serves as a major component of biological membranes and animal phospholipids. It is synthesized from dietary linoleic acid and acts as a precursor to lipid mediators such as prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Arachidonic acid can improve cognitive responses and cardiovascular function and is commonly used to induce paw edema models. |
| Targets&IC50 | Mg2+-ATPase:90 μM, 3H-ouabain:32 μM, NaK-ATPase:75 μM, L-type Ca2+ channel (cardiac myocytes):8.5 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: RAW264.7 and PBMC-derived macrophages were treated with Arachidonic acid (40-80 µM) for 12-24 h and cell viability was determined by CCK8 assay. RESULTS: Arachidonic acid significantly inhibited macrophage viability in a dose-dependent manner within 12 h, and more inhibition was observed between 12 h and 24 h. Arachidonic acid was also shown to inhibit macrophage viability in a dose-dependent manner. [1] METHODS: Human breast cancer cells, MDA-MB-231, were treated with Arachidonic acid (8 µM) for 48 h. Caspase activity was measured using a spectrofluorophotometer. RESULTS: MDA-MB-231 cells stimulated with Arachidonic acid for 48 h showed a significant increase in caspase-3 activity, and Arachidonic acid also induced significant activation of caspase-8 and caspase-9. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To test the effect on the inflammatory response, Arachidonic acid (150 mg/kg in 1% CMC Na) was administered orally to C57BL/6 mice with high-fat diet (HFD)-induced cardiac injury every two days for eight weeks. RESULTS: Arachidonic acid treatment prevented MD2/TLR4 dimerization, induction of inflammatory factors, and tissue damage through TLR4-mediated inflammatory responses in a high-fat diet obese mouse model. [3] |
| Synonyms | Vevodar, Immunocytophyte, Immunocytophyt, arachidonate |
| Molecular Weight | 304.47 |
| Formula | C20H32O2 |
| Cas No. | 506-32-1 |
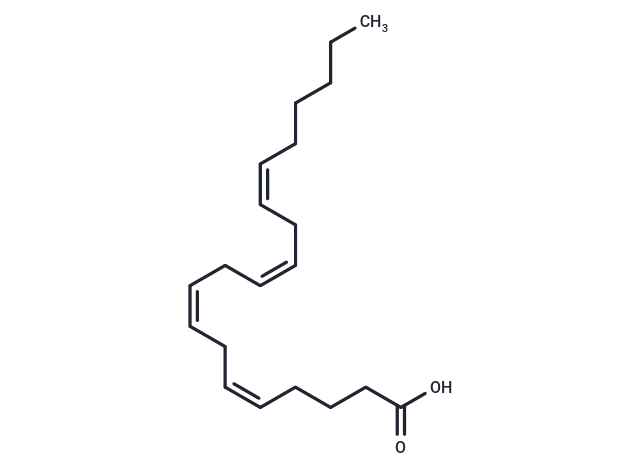
| Smiles | CCCCC\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/CCCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 0.922 g/cm3 at 25℃ (lit.) |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,store under nitrogen,keep away from moisture,store at low temperature | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 262.5 mg/mL (862.15 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 10 mg/mL (32.84 mM), Suspension. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.