 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

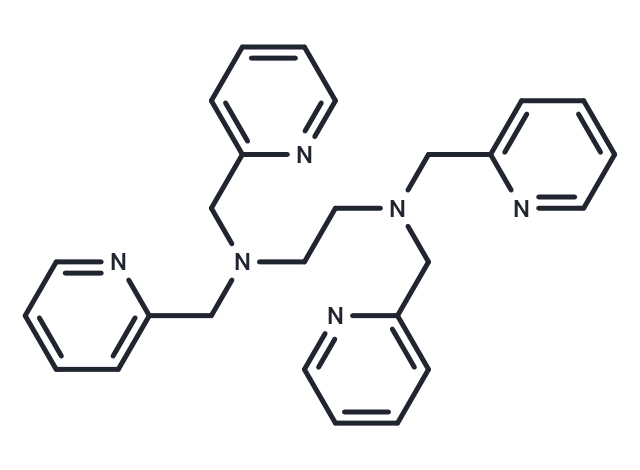
TPEN (TPEDA) is a specific cell-permeable heavy metal chelator.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $38 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $54 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $80 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $117 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | TPEN (TPEDA) is a specific cell-permeable heavy metal chelator. |
| In vitro | TPEN attenuates Fura-2 fluorescence changes induced by cadmium, mercury, and methylmercury. In cells stimulated with cadmium chloride (10/30 μM), the addition of TPEN at 3 h after exposure significantly decreases the elevated Fura-2 fluorescence ratio to the basal levels within 10 min (119.6±2.4% or 109±1.5% decrease in ΔRatio (F340/F380)). TPEN targets colon cancer cells through redox cycling of copper. TPEN dose- and time-dependently reduces cell viability. TPEN-induced cell death is also dependent on the redox cycling of copper since the copper chelator neocuproine inhibited DNA damage and reduced pChk1, γ-H2AX, and ATM protein expression. |
| Kinase Assay | In a 96-well-plate, 40 nM USP2, 40 nM USP7, or 20 nM SENP2 is preincubated with a concentration range of NSC 632839 (NCI/NIH developmental therapeutics program) or control for 30 min before supplementation with an equal volume of 60 nM Ub-PLA2/40 μM NBD C6-HPC (USP2 or 7) or 20 nM SUMO3-PLA2/40 μM NBD C6-HPC (SENP2). Relative activity of the enzymes is determined by measuring the RFU values at single time points within the initial linear range (USP, 50 min; USP7, 50 min; and SENP2, 30 min). The RFU values within the initial linear range are normalized such that isopeptidase+vehicle=0% inhibition and isopeptidase+NEM=100% inhibition. The EC50 values are determined as above. The inhibitory activity of the test compound against the reporter enzyme PLA2 is performed as described above except there is no preincubation step and the data are normalized such that free PLA2+vehicle=0% inhibition and free PLA2+EDTA=100% inhibition. PLA2 activity is determined 8 min after the addition of the reagents[1]. |
| Cell Research | TPEN is dissolved in DMSO and then diluted with appropriate medium[1]. Human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y, are grown in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) mixed 1:1 with Ham's F-12 nutrient mixture containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 unit/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin at 37°C in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere. Two days before experimentation, cells are seeded at a density of 7×104 cells/cm2 in a 96-well plate. Cells in a 96-well plate are serum-starved for 4 hr; calcium indicator fura-2 is then loaded into the cells by using Calcium kit II fura-2. In brief, SH-SY5Ycells are incubated with 5 μM fura-2/AM in the presence of 0.04% Pluronic F-127, a dispersing agent to improve the efficiency of loading with fura-2, and 1.25 mM probenecid, a blocker of organic anion transport to prevent leakage of fura-2 from cells. After 1 hr incubation at 37°C, fura-2 fluorescence is measured at 500 nm emission after excitation at 340 nm (F340) or 380 nm (F380) using an Infinite M200 plate reader at 37°C.The change in [Ca2+]i is reflected by the ratio of F340 and F380. To determine the changes in fura-2 fluorescence ratio induced by heavy metal compounds, cells are treated with manganese chloride, lead acetate, cadmium chloride , mercuric chloride and MeHg chloride dissolved in distilled water. We confirmed that the cells adhered to the bottom of the plate after 6 hr exposure to heavy metal compounds. The cells are also treated with three Ca2+ channel blockers, lanthanum chloride dissolved in distilled water, verapamil and 2-APB dissolved in DMSO, 30 min before heavy metal exposure. The heavy metal chelator TPEN is dissolved in DMSO and added 3 hr after the stimulation with heavy metals to determine the contribution of endogenous and exogenous heavy metals on fura-2 fluorescence changes.We measured the effect of TPEN (20 μM) on the fura-2 fluorescence ratio after a 10 min treatment with TPEN, since our preliminary experiments showed that the effect of TPEN on fura-2 fluorescence reached maximum and stabilized within 10 min of the treatment[1]. |
| Synonyms | TPEDA |
| Molecular Weight | 424.54 |
| Formula | C26H28N6 |
| Cas No. | 16858-02-9 |
| Smiles | C(CN(Cc1ccccn1)Cc1ccccn1)N(Cc1ccccn1)Cc1ccccn1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.3893 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 20 mg/mL (47.11 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (4.71 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.