Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Rosmarinic acid (Labiatenic acid) is widely found in plants and has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial activities. It inhibits MAO-A, MAO-B, and COMT with IC50 of 50.1, 184.6, and 26.7 μM respectively.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $36 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $68 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $159 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $237 | - | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $589 | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Rosmarinic acid (Labiatenic acid) is widely found in plants and has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial activities. It inhibits MAO-A, MAO-B, and COMT with IC50 of 50.1, 184.6, and 26.7 μM respectively. |
| Targets&IC50 | IKKβ:12 μM |
| In vitro | Rosmarinic acid (RA) exhibits a multifunctional profile characterized by antioxidant effects, and monoamine oxidases (MAO-A and MAO-B) and catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) inhibition in vitro. Rosmarinic acid exhibits antioxidant effects against hydroxyl (HO(•)) and nitric oxide (NO) radicals (IC50 of 29.4 and 140 μM, respectively), and inhibition of lipid peroxidation (IC50 of 19.6 μM)[1]. Rosmarinic acid (RA) exerts a significant cytoprotective effect by scavenging intracellular ROS induced by UVB. In Water2-treated cells, 2.5 μM Rosmarinic acid scavenges 60% of intracellular ROS compared to 77% of intracellular ROS scavenging effect in N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC)[2]. |
| In vivo | Rosmarinic acid (RA), a prevalent phenolic ester found extensively in the Labiatae family of herbs such as Rosmarinus officinalis, Salvia miltiorrhiza, and Prunella vulgaris, effectively mitigates colonic inflammation in mice induced with dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) through the dual inhibition of NF-κB and STAT3 pathways. Administering Rosmarinic acid (30, 60 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly reduces cytokine production in the DSS-induced colitis model. |
| Cell Research | Rosmarinic acid (RA) is dissolved in DMSO and stored, and then diluted with appropriate media before use[2]. Human keratinocytes (HaCaT cells) are treated with Rosmarinic acid (0.625, 1.25, 2.5, or 5 μM) and exposed to UVB radiation 1 h later. They are then incubated at 37°C for 48 h. At this time, MTT is added to each well to obtain a total reaction volume of 200 μL. After 4 h incubation, the supernatant is removed by aspiration. The formazan crystals in each well are dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; 150 μL), and the absorbance at 540 nm is measured on a scanning multi-well spectrophotometer[2]. |
| Synonyms | Rosemary acid, Labiatenic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 360.31 |
| Formula | C18H16O8 |
| Cas No. | 20283-92-5 |
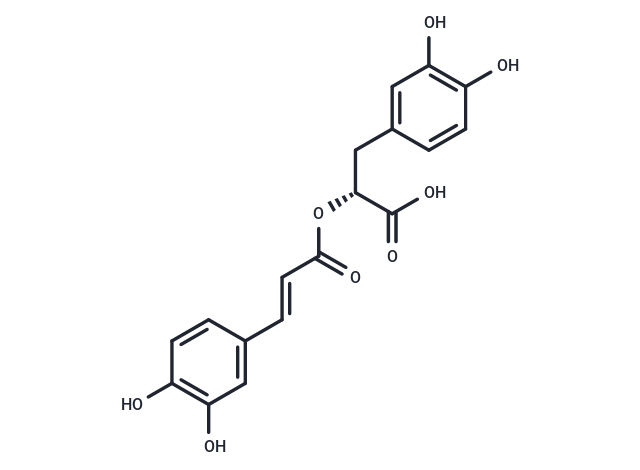
| Smiles | C([C@@H](OC(/C=C/C1=CC(O)=C(O)C=C1)=O)C(O)=O)C2=CC(O)=C(O)C=C2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.33 g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,keep away from moisture,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 36.03 mg/mL (100 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 72.07 mg/mL (200.02 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 5% DMSO+95% Saline: 1.5 mg/mL (4.16 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.