Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Pepstatin (Pepsin Inhibitor S 735A) is an aspartate protease inhibitor that also inhibits HIV protease activity with specific and oral activity. Pepstatin inhibits autophagy.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $32 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $98 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $166 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $273 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $397 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $48 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Pepstatin (Pepsin Inhibitor S 735A) is an aspartate protease inhibitor that also inhibits HIV protease activity with specific and oral activity. Pepstatin inhibits autophagy. |
| Targets&IC50 | Hemoglobin-proctase:6.2 nM, Casein-pepsin:150 nM, Hemoglobin-acid protease:260 nM, Casein-acid protease:520 nM, Casein-proctase:290 nM, Hemoglobin-pepsin:4.5 nM |
| In vitro | METHODS: F. pedrosoi sclerotic cells were treated with Pepstatin (0.1-20 µM) for 20 h and cell viability was measured by CFU assay. RESULTS: Pepstatin was able to block the viability of sclerotic cells in a typical dose-dependent manner. [1] METHODS: SV40-transformed skin fibroblasts were treated with Pepstatin (100 µM) for 1 h, then incubated with doxorubicin (1 µM) or TNF-α (50 ng/mL) in 1% FCS for 48 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay. RESULTS: Cathepsin D activity was strongly inhibited by pretreatment of human cells with 100 µM Pepstatin. Despite this inhibition, cell death induced by doxorubicin or TNF-α in fibroblasts was not prevented by Pepstatin. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To examine the kinetics of inhibition in vivo, pepstatin (25-200 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to CD-1 mice. RESULTS: In the liver, significant inhibition of cathepsin D persisted for at least 15 days, whereas in the heart and skeletal muscle this inhibition lasted for a much shorter period. The return of enzyme activity to normal values was dose-dependent, and there were significant differences in the recovery of enzyme activity in these organ tissues at the same dose level, with the liver being the most sensitive. [3] |
| Cell Research | Pepstatin A is freshly dissolved in DMSO at 7 mM. It is very slowly diluted (1:100) into the medium of HIV-infected H9 suspension cultures so that no pepstatin A precipitated (final concentration, 70 μM pepstatin A and 1% DMSO), and the cultures are incubated without change of culture medium for 48 hr. As a control, uninfected H9 cells are also incubated with pepstatin and in addition HIV infected and uninfected cells are incubated with 1% DMSO but without pepstatin [2]. |
| Animal Research | To investigate the effect of pepsins on bacterial motility, similar experiments were performed, but the pepsin in the stomach was inactivated by rinsing the stomach with pepstatin (100 μl of a 2-mg/ml stock solution). Samples were taken and analyzed for bacterial motility at the test pH values of 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 4.5, and 5.0 and at the same periods after application of the bacterial suspension as in the experiments with active pepsins [4]. |
| Synonyms | Pepstatin A, Pepsin Inhibitor S 735A, Ahpatinin C |
| Molecular Weight | 685.89 |
| Formula | C34H63N5O9 |
| Cas No. | 26305-03-3 |
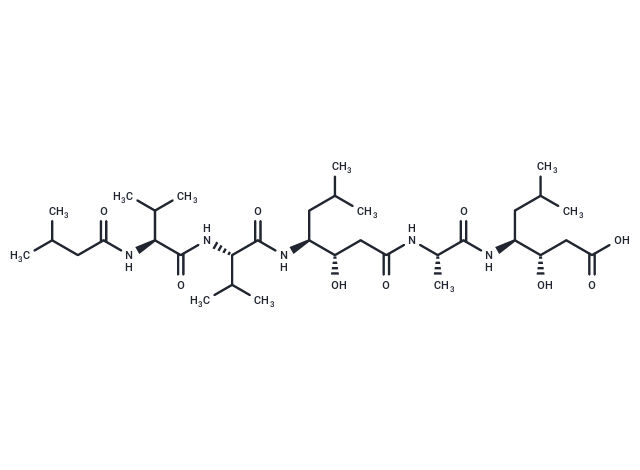
| Smiles | CC(C)C[C@H](NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)C[C@H](O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)CC(C)C)C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.117 g/cm3 |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Sequence | IsoValeryl-Val-Val-Sta-Ala-Sta-OH |
| Sequence Short | IsoVeryl-VV-Sta-A-Sta-OH |
| Storage | keep away from moisture | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 1 mg/mL (1.46 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: Insoluble DMSO: 32 mg/mL (46.65 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (2.92 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.