Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Icosabutate is a structurally engineered and orally active ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid. Icosabutate is well tolerated, and efficacious in lowering non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) levels in persistent hypertriglyceridemia.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 332.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 1,080.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 1,410.00 | |
| 100 mg | 6-8 weeks | $ 1,990.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 333.00 |

| Description | Icosabutate is a structurally engineered and orally active ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid. Icosabutate is well tolerated, and efficacious in lowering non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) levels in persistent hypertriglyceridemia. |
| In vivo | Icosabutate ([14‐C]‐icosabutate; p.o.; 100 mg/kg; once) displays that peak concentrations of radioactivity in most tissues at 4‐8 hours after the dose (except the gastrointestinal tract) with highest concentrations in the liver and kidney, most other tissues contain levels of radioactivity below that in plasma in male albino Wistar rats. Icosabutate (p.o.; 100 mg/kg; once) accounts for the much higher flow rate of portal vein plasma (522?mL/h) versus mesenteric lymph (0.5?mL/h), that data show that icosabutate is almost entirely taken up through the portal vein (>99%) with only a small fraction of icosabutate being absorbed through the lymphatic pathway in 8‐week old male Wistar rats. Icosabutate (p.o.; 112?mg/kg/day; 20 weeks) prevents microvesicular steatosis (-35%) and hepatocellular hypertrophy (-82%), but not macrovesicular steatosis. Despite comparable decreases in hepatic inflammatory cell aggregates, only icosabutate reduced hepatic collagen content, after 20 weeks of treatment. Icosabutate (diet administration; 135?mg/kg/day; 5?weeks) markedly improved glucose tolerance after an oral glucose load, significantly reduces AUC (0‐120 minutes) by 60% without affecting body weight, reduce plasma alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels improves glucose metabolism by a significant decrease in blood glucose, blood hemoglobin A1c, plasma insulin, and HOMA‐IR (-50%, -47%, -76% and -87%, respectively) in mice [1]. |
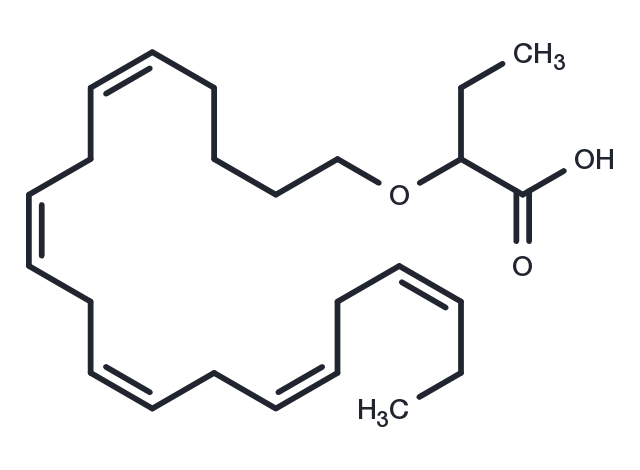
| Molecular Weight | 374.56 |
| Formula | C24H38O3 |
| CAS No. | 1253909-57-7 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Icosabutate 1253909-57-7 Others inhibitor inhibit
