Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
H-89 is a selective and potent protein kinase A inhibitor (IC50: 48 nM), a candidate cardioprotectant, induces spatial learning impairment in rats, and can be used to study myocardial infarction.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $34 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $54 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $116 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $178 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $267 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $659 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $37 | In Stock |
| Description | H-89 is a selective and potent protein kinase A inhibitor (IC50: 48 nM), a candidate cardioprotectant, induces spatial learning impairment in rats, and can be used to study myocardial infarction. |
| Targets&IC50 | protein kinase A:48 nM |
| In vitro | Pretreatment of PC12D cells with H-89 (30 μM) significantly inhibited cAMP-dependent histone IIb phosphorylation activity in cell lysates, but did not affect other protein phosphorylation activities [1]; in rat skin EDL fibers , H-89 (10 μM) only slightly inhibited the force response to depolarization; H-89 (1-2 μM) significantly slowed the re-excitation rate in rat skin EDL fibers, most likely because of its Deleteriously affects the T system potential; H-89 (10-100 μM) also inhibits the net uptake of Ca2+ by SR. [2] |
| In vivo | b>METHODS: H-89 (0.05, 0.1, 0.2 mg/100 g, intraperitoneal injection) was used 30 minutes before the infusion of pentylene tetrazolium (PTZ) in mice to study the effect of H-89 on Bucladesine-induced epileptic activity in PTZ-treated mice. RESULTS: H-89 (0.2 mg/100 g) significantly increased the seizure latency and threshold of PTZ-treated animals; H-89 (0.05, 0.2 mg/100 g) blocked the epileptogenic activity of Bucladesine and significantly increased the seizure latency and seizure threshold. [3] |
| Synonyms | Protein kinase inhibitor H-89 |
| Molecular Weight | 446.36 |
| Formula | C20H20BrN3O2S |
| Cas No. | 127243-85-0 |
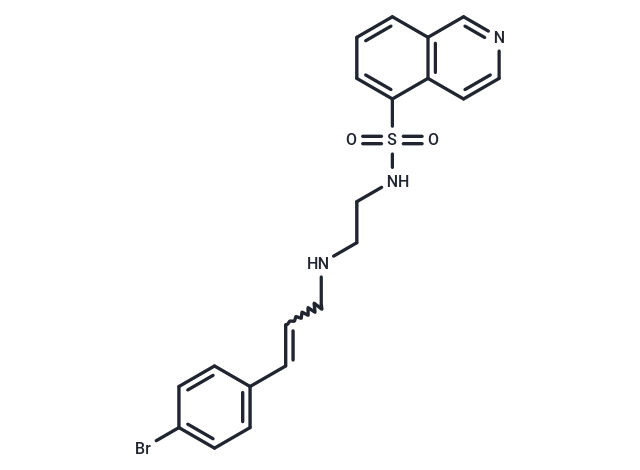
| Smiles | O=S(=O)(NCCNCC=CC1=CC=C(Br)C=C1)C2=CC=CC=3C=NC=CC32 |
| Relative Density. | 1.436 g/cm3 |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 72 mg/mL (161.3 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.