Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
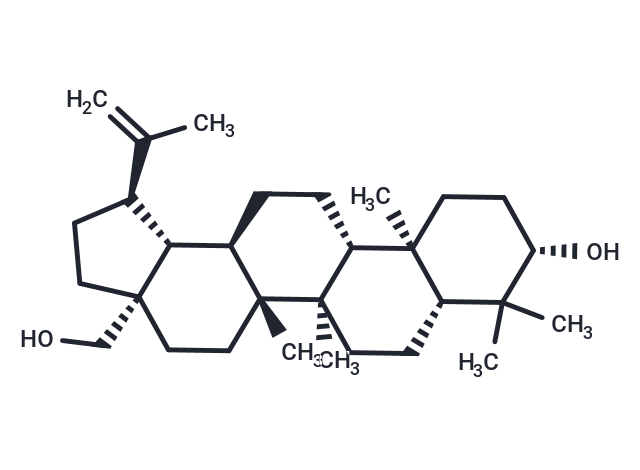
Betulin (betulinol) (lup-20(29)-ene-3β, 28-diol) is an abundant, naturally occurring triterpene. It is commonly isolated from the bark of birch trees where it forms up to 30% of the dry weight of the extractive and is found in birch sap as well.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $33 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $50 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $72 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Betulin (betulinol) (lup-20(29)-ene-3β, 28-diol) is an abundant, naturally occurring triterpene. It is commonly isolated from the bark of birch trees where it forms up to 30% of the dry weight of the extractive and is found in birch sap as well. |
| Targets&IC50 | SREBP:14.5 μM |
| In vitro | Betulin (BE) is recognized for its extensive biological and pharmacological benefits, notably its anticancer and chemopreventive capabilities, which have garnered substantial interest. Research indicates that BE impedes the growth of cancer cells across various cancer types, showing a range of antiproliferative effects—from minimal in human erythroleukaemia cells (K562) to pronounced in human neuroblastoma cells (SK-N-AS). Additionally, BE demonstrates marked cytotoxicity towards primary cancer cell cultures from ovarian, cervical carcinoma, and glioblastoma, with IC50 values between 2.8 to 3.4 μM, notably lower than those in established cell lines. Comparative studies of crude birch bark extract, alongside purified betulin and betulinic acid, reveal significant efficacy against human gastric carcinoma (EPG85-257) and human pancreatic carcinoma (EPP85-181), including drug-sensitive and drug-resistant types, indicating their potential as promising therapeutic agents for cancer treatment. |
| In vivo | Betulin enhances glucose intolerance, augments basal learning performance, and notably ameliorates oxidative stress by significantly restoring SOD activity while reducing MDA levels in the hippocampus. Further, it significantly mitigates serum and hippocampal inflammatory cytokines. Betulin administration also upregulates Nrf2 and HO-1 expressions and inhibits IκB and NF-κB phosphorylations. Overall, Betulin potentially offers cognitive protection against STZ-induced diabetes in rats through the HO-1/Nrf-2/NF-κB pathway[3]. |
| Cell Research | Chemoresistance is tested using a proliferation assay based on sulphorhodamine B staining. Briefly, 800 cells per well are seeded in triplicate in 96-well plates. After attachment for 24 h, substances are added in dilution series for a 5-day incubation, before SRB staining is performed. Incubation is terminated by replacing the medium with 10% trichloroacetic acid, followed by further incubation at 4°C for 1h. Subsequently, the plates are ished five times with water and stained by adding 100 μL 0.4% SRB in 1% acetic acid for 10 min at room temperature. Ishing the plates five times with 1% acetic acid eliminated unbound dye. After air-drying and re-solubization of the protein bound dye in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH=8.0), absorbance is read at 562 nm[2]. |
| Synonyms | Trochol, Betulol, betulinol, betulinic alcohol, betuline |
| Molecular Weight | 442.72 |
| Formula | C30H50O2 |
| Cas No. | 473-98-3 |
| Smiles | CC(=C)[C@@H]1CC[C@]2(CO)CC[C@]3(C)[C@H](CC[C@@H]4[C@@]5(C)CC[C@H](O)C(C)(C)[C@@H]5CC[C@@]34C)[C@@H]12 |
| Relative Density. | 1.017g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 20 mg/mL (45.18 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.