Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

BAY 41-4109 is a potent inhibitor of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) with an IC50 of 53 nM.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $386 | 5 days | |
| 25 mg | $2,270 | 6-8 weeks | |
| 50 mg | $2,980 | 6-8 weeks | |
| 100 mg | $4,180 | 6-8 weeks |
| Description | BAY 41-4109 is a potent inhibitor of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) with an IC50 of 53 nM. |
| Targets&IC50 | HBV:53 nM |
| In vitro | BAY 41-4109 effectively accelerates and alters the direction of capsid assembly in vitro, demonstrating potent inhibitory effects on both HBV DNA release and cytoplasmic HBcAg levels, with IC50 values of 32.6 and 132 nM in HepG2.2.15 cells, respectively. Its inhibitory action on HBV DNA and HBcAg is dose-dependent, underscoring that its anti-HBV properties hinge on the rate at which HBcAg is inhibited. Additionally, BAY 41-4109 can stabilize preformed capsids, achieving a stabilization ratio of one inhibitor molecule per two dimers. |
| In vivo | BAY 41-4109 effectively suppresses virus production in vivo through a mechanism focusing on the viral capsid[2]. It dose-dependently decreases viral DNA in both the liver and plasma, showing efficacy on par with 3TC, and it diminishes hepatitis B virus core antigen (HBcAg) in the livers of HBV-transgenic mice. Pharmacokinetic evaluations in mice reveal quick absorption, 30% bioavailability, and dose-proportional plasma concentrations, reaching approximately 60% in rats and dogs[1]. |
| Molecular Weight | 395.76 |
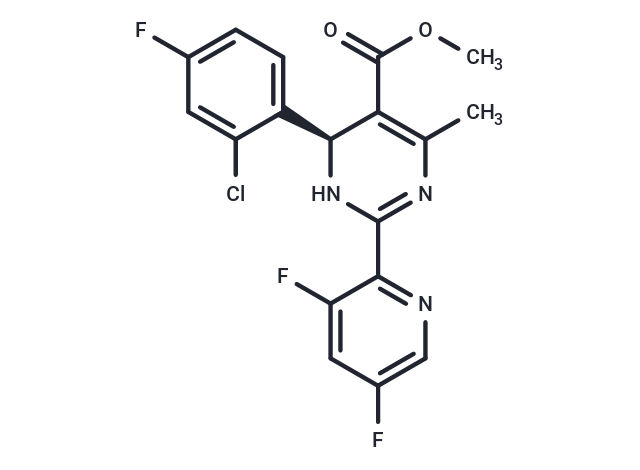
| Formula | C18H13ClF3N3O2 |
| Cas No. | 298708-81-3 |
| Relative Density. | 1.46 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (252.68 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.