Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


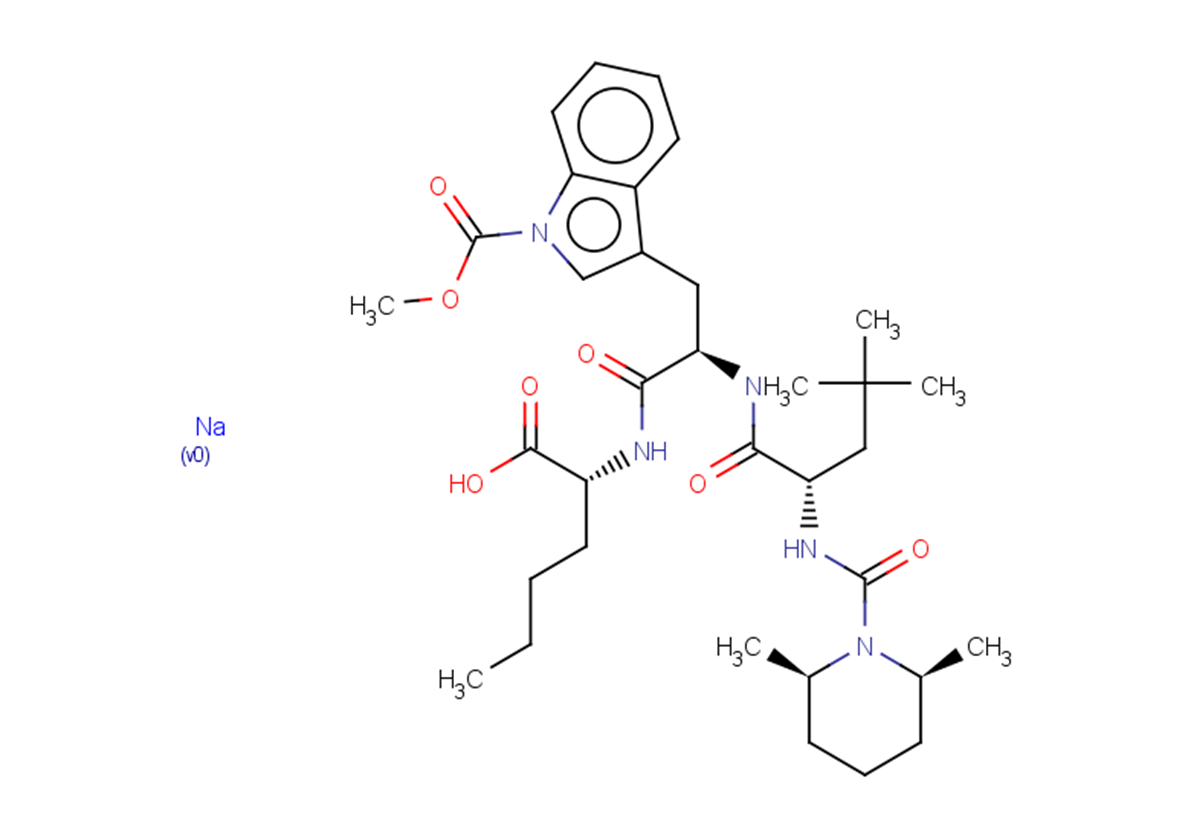
BQ-788 sodium salt is a potent and selective antagonist of ETB receptor(ETB receptors with an IC50 of 1.2 nM in human Girrardi heart cells).
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | 5 days | $ 285.00 | |
| 25 mg | 10-14 weeks | $ 977.00 | |
| 50 mg | 10-14 weeks | $ 1,270.00 | |
| 100 mg | 10-14 weeks | $ 1,930.00 |
| Description | BQ-788 sodium salt is a potent and selective antagonist of ETB receptor(ETB receptors with an IC50 of 1.2 nM in human Girrardi heart cells). |
| Targets&IC50 | ETB:1.2 nM |
| In vitro | BQ-788 potently and competitively inhibits 125I-labeled ET-1 binding to ETB receptors in human Girrardi heart cells (hGH) with an IC50 of 1.2 nM. However, it only poorly inhibits the binding to ETA receptors in human neuro-blastoma cell line SK-N-MC cells (IC50, 1300 nM). BQ-788 also inhibits several bioactivities of ET-1, such as bronchoconstriction, cell proliferation, and clearance of perfused ET-1[1]. BQ-788 shows no agonistic activity up to 10 μM and competitively inhibits thevasoconstriction induced by an ETB-selective agonist (pA2, 8.4). |
| In vivo | Administered intravenously at a dosage of 3 mg/kg/h, BQ-788 effectively blocks the ETB receptor-mediated depressor responses induced by pharmacological levels of ET-1 or sarafotoxin6c (0.5 nmol/kg) in conscious rats, without affecting pressor responses. In Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats, this dosage of BQ-788 results in a significant increase in blood pressure, approximately 20 mm Hg. Moreover, BQ-788 is noted to inhibit ET-1-induced bronchoconstriction, tumor proliferation, and lipopolysaccharide-triggered organ failure. It notably shifts the ET-1 dose-response curve eightfold to the left, highlighting a substantial role of ETB dilator receptors. Additionally, BQ-788 significantly raises plasma ET-1 levels, indicating its potential as an ETB receptor blocker in vivo. In mice, intraplantar administration of 30 nmol BQ-788 reduces mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia, oedema, and myeloperoxidase activity by significant margins, alongside diminishing overt pain-like behaviors. Likewise, intraplantar interventions with either clazosentan or BQ-788 lower superoxide anion production and lipid peroxidation in both spinal and peripheral contexts. |
| Molecular Weight | 664.8 |
| Formula | C34H51N5NaO7 |
| CAS No. | 156161-89-6 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 43 mg/mL (64.78 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
BQ-788 sodium salt 156161-89-6 Others BQ788 sodium salt BQ 788 sodium salt BQ-788 sodium inhibitor inhibit
