Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Azilsartan Medoxomil (TAK-491) is an orally administered angiotensin II receptor type 1 antagonist with IC50 of 0.62 nM, which used in the treatment of adults with essential hypertension.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | 32 € | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | 45 € | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | 76 € | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | 115 € | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | 210 € | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | 353 € | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | 521 € | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | 1.111 € | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | 92 € | In Stock |
| Description | Azilsartan Medoxomil (TAK-491) is an orally administered angiotensin II receptor type 1 antagonist with IC50 of 0.62 nM, which used in the treatment of adults with essential hypertension. |
| Targets&IC50 | Ang II type 1 receptor:0.62 nM |
| In vitro | Azilsartan medoxomil is a prodrug, which is rapidly converted to the active moiety, azilsartan (TAK-536), by ester hydrolysis in the gut and plasma during absorption after oral administration. Azilsartan selectively blocks the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 (angiotensin II type 1) receptors found in the vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland, thereby promoting vasodilation and a decrease in the effects of aldosterone. [2] Azilsartan is a highly selective antagonist to the AT1 receptor, with an IC50 of 2.6 nM, exhibiting a >10,000-fold affinity for the AT1 receptor compared with the AT2 receptor, and has not shown affinity for other cardiac receptors or ion channels. The inhibitory effect of Azilsartan persists after washout of the free compound (IC50 value of 7.4 nM). Azilsartan also inhibits the accumulation of angiotensin II -induced inositol 1-phosphate (IP1) in the cell-based assay with an IC50 value of 9.2 nM, and this effect is resistant to washout (IC50 value of 81.3 nM). [1] |
| Kinase Assay | Radioligand Binding: A radioligand binding assay is performed by using human AT1 receptor-coated microplates containing 4.4 to 6.2 fmol of receptors/well (10 μg of membrane protein/well). Membrane-coated wells are incubated with 45 μl of assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, and 0.005% CHAPS, pH 7.4) containing various concentrations of test compounds at room temperature. After 90 min, 5 μl of 125I-Sar1-Ile8-AII (final concentration 0.6 nM) dissolved in assay buffer is added to the wells, and the plate is incubated for 5 h. In each step, the plate is briefly and gently shaken on a plate shaker. |
| Cell Research | Measurement of Inositol 1-Phosphate Accumulation. Twentyfour hours after transfections with human AT1-expressing plasmids, the cells are starved by changing the culture medium to starvation buffer (1 mM CaCl2, 0.5 mM MgCl2, 4.2 mM KCl, 146 mM NaCl, 5.5 mM glucose, and 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.3). Then, 5 μl/well of the test compounds dissolved in starvation buffer is added to the cells at the indicated concentrations, and they are pretreated for the indicated times. Two hours after starvation, LiCl is added to a final concentration of 50 mM with or without angiotensin II 10 nM, and the cells are further incubated for the indicated times at 37°C. In washout experiments, the cells are washed once with 100 μl/well of starvation buffer to remove unbound compounds before stimulation with angiotensin II. The accumulation of inositol 1-phosphate (IP1) is measured by using a IP-One Tb kit. The fluorescence resonance energy transfer signal is measured on a plate reader.(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | TAK-491 |
| Molecular Weight | 568.53 |
| Formula | C30H24N4O8 |
| Cas No. | 863031-21-4 |
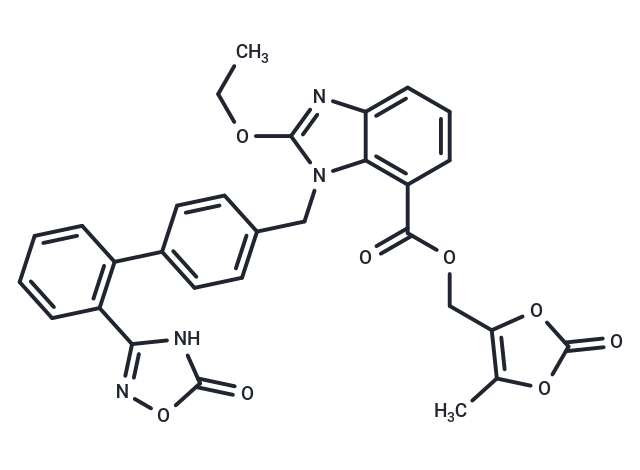
| Smiles | C(N1C=2C(N=C1OCC)=CC=CC2C(OCC=3OC(=O)OC3C)=O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C5=C(C=CC=C5)C=6NC(=O)ON6 |
| Relative Density. | 1.45 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 105 mg/mL (184.69 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.